| On this page |
In order to use Houdini Engine, a Houdini Engine session needs to be created. Creating the session will load the necessary Houdini libraries and plug-ins and then setup Houdini Engine according to various preferences and environment variables.
Automatic Session ¶
When the plug-in is started up, it will automatically create an out-of-process session to use.
The automatic session uses a named pipe with the name of HEMAX_AutoPipeServer.

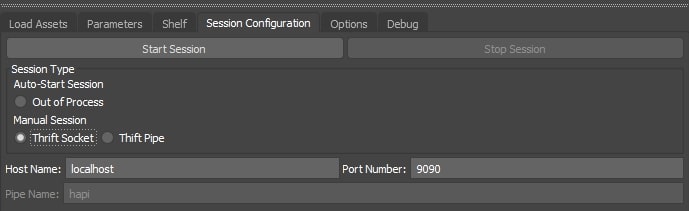
Manual Session ¶
There is also the option to manually connect to a specified session via a Thrift socket or a Thrift named pipe. This is done via the use of a thin client that is included in Houdini Engine. In short, this thin client allows the main Houdini Engine processing to happen in a separate process (outside of the 3ds Max process). The plug-in can use either a TCP socket or a named pipe to communicate between the 3ds Max process and the Houdini Engine process.
Note that creating a manual session requires a Houdini Engine server process that the session can communicate with. For more information about running HARS, please visit the Houdini Engine documentation
Socket ¶
In order to use socket sessions, a Houdini Engine server must be manually started with a known port on a known machine. Then, that host and port information can be used in the plug-in to connect to that session.
The easiest way to create a Houdini Engine server is to create a debugging session within Houdini. This can be found under the Windows → Houdini Engine Debugger menu found within Houdini.
Named Pipe ¶
A named pipe connection is the recommended method when starting the thin client on the same local machine. Just like a socket session, a Houdini Engine server must be manually started with a known pipe name. That pipe name can then be used in the plug-in to connect to that session.
