| On this page |
Old network
Houdini20.5以降、Compositingノードの代わりにCopernicusノードが使用されるようになりました。
これらのネットワークは両方ともまだ存在していますが、CompositingネットワークはもはやCOP Network - Oldに指定されました。
Compositingネットワークとそのノードは廃止され、将来のHoudiniリリースで削除される予定です。
このノードは、ライトを画像に追加します。 ライトには、指向性または非指向性があり、アンビエント、スペキュラ、ディフューズのコンポーネントを持ちます。 画像は、フラットな画像、バンプマップのある画像、ポイント/法線平面を含んだディープラスタ画像にすることができます。
Flat Lighting ¶
Flat照明には余分な情報は必要ありません。画像はフラットな平面であると想定し、照明均衡をピクセルに適用します。 画像は(0,0,0) から (1,1,0)の領域を占めます。
ライトの位置には、プラスのZ値が必要です。画像の中心は(0.5, 0.5, 0)です。 Z=0からのライトの距離により、輝度および(円錐曲線が使用されている場合)ライトの形状が決定します。
Bump Map Lighting ¶
Bump Map照明にはバンプマップが必要で、これはBump COPにより作成できます。 この照明タイプは、Flat照明に似ていますが、バンプマップに基づいて、サーフェス法線に摂動が与えられている点が異なります。
バンプの高さを調整するには、Bright COPによりバンプマップに明暗をつける必要があります。 もしくは、バンプマップをBump COPにより作成した場合は、Bump Heightパラメータを調整します。
Deep Raster (3D) Lighting ¶
3D照明は、PointおよびNormalマップを使用して実行します。 これらのマップは、Mantra ROPのDeep Rasterタブから生成できます。 Pointマップのみが存在する場合、Lighting COPはポイントの位置から法線を作成しようとします。 Normalマップのみが存在する場合、Bump Map照明に似た処理が行なわれ、ポイントは(0,0,0)から(1,1,0)の範囲にあると想定されます。
ライトは、3Dポイントに対して、どこの位置にでも配置できます。 3Dポイント値の決定にビューポート検知関数(i)を使用すると、より正確な位置にライトを配置できるため、便利です。
Volumetric Lighting ¶
Volumetric照明は、上記のすべての照明技術と一緒に使用できますが、3D照明と組み合わせると最も効果的です。 Volumetric照明は、環境ライト散乱効果を追加するため、ライトの円錐が見えるようになります。
この照明の計算にはかなり時間がかかるため、他の照明パラメータの設定をすべて最初に行なってから、このオプションを有効にすることをお勧めします。
アルファ平面がスコープされている場合、各ポイントのライトの量はその中に配置されます。
Overloading VEXパラメータ ¶
このノードはVEXで実行され、パラメータの上書きをサポートしています。 1番目の入力に操作パラメータのチャンネル名に一致する平面がある場合、入力平面はパラメータの値として使用され、効率的にパラメータを上書きします。 上書きされたパラメータは、各ピクセルベースで平面から評価されます。
例: 入力COPに下記の平面がある場合:
C{r,g,b}
A
fogdensそして、入力COPがVEX Fog COPに送られる場合、霧密度は、fogdens平面により各ピクセルで決定されます。
これは、Fog Densityパラメータのチャンネル名が'fogdens'チャンネル名と一致するためです。
スコーピング ¶
この操作は、一定の平面や平面のコンポーネントに限定できます。 また、シーケンス内のフレームのサブセットに適用できます。 画像には、修正を行なうスコープされたフレームと平面の両方が必要です。
修正されない画像は通過するため、メモリや処理時間を必要としません。
Masking ¶
この操作はマスキングが可能で、その操作を画像の領域に制限します。 マスクは反転させたり、明るくしたり、暗くしたりすることができます。
マスク入力はノードの横にあります。コネクタのラベルはマスクとして使用する平面を示します。
マスク入力は、出力画像の解像度と異なる場合、出力画像の解像度に合わせてスケールもできます。
このノードが断続的に変化していても、マスクが変化していない場合、Scale COPを配置すると、マスク画像のサイズ変更がやや速くなります。
これを行なわない場合は、このノードを処理する度に毎回スケールが発生します。
パラメータ ¶
Lighting ¶
Surface Type
使用するサーフェス照明のタイプ:
Flat
画像には均一な法線と均一なデプスがあります。
Bump Map
画像にはパンプ法線と均一なデプスがあります。
Point & Normal
画像には3D照明用の法線とポイントマップがあります。
Point Only
画像には擬似3D照明用のポイントマップがあります。
Normal Map
画像には均一なデプスとさまざまな法線があります。
Eye Distance
目線から(Z=0での)画像までの距離です。
Ambient
ライトの環境コンポーネントです。
Diffuse
ライトの拡散コンポーネントです。
Specular
ライトのスペキュラコンポーネントです。
Correct for Aspect Ratio
画像が正方形でない場合、これは、スポットライトが円形のままになるように座標を調整します。
Color Operation
既存の画像にライトを適用する方法:
Light Existing Color
画像のカラーがサーフェスのカラーとして使用され、照明の計算によりそのカラーが置き換わります。
Add to Existing Color
画像のカラーがサーフェスのカラーとして使用され、そのカラーに照明の計算が追加されます。
New Lighting Only
画像のカラーは無視され、新しい照明に置き換わります。これは、環境、拡散、スペキュラカラーのみを表示します。
Material ¶
このタブでは、拡散およびスペキュラモデルを変更することができます。
Diffuse Model
使用する拡散モデルのタイプ:
Simple
簡単な内積モデル。
Oren-Nayar
粘土のようなきめの粗いマテリアルモデル。
Diffuse Roughness
Oren-Nayarモデルの粗さ。
Specular Model
使用するスペキュラモデルで、PhongまたはBlinnです。
Exponent
Phongスペキュラ指数です。
Roughness
Blinn粗度パラメータです。
Light ¶
ライトの位置と方向。
Position
ライトの位置です。Flat、Bump Map、Normal Mapモードでは、画像の座標は{0,0,0} (左下) から {1,1,0} (右上)です。
Attenuation
ライトが50%の強度になる距離です。
Directional Light
オンの場合、ライトは方向を持ちます。
Direction
ライトの方向ベクトルです。
Cone
度数単位のライトの円錐サイズです。
Cone Falloff
度数単位のライトのフォールオフ円錐サイズです。
Falloff
ライトのフォールオフ関数です。
Volumetric ¶
ボリューメトリックライトの効果を追加します。この計算にはかなりの時間がかかります。
Atmosphere Scatter
大気によるライトの散乱量です。数字が大きいと、もやのかかったライトが作成されます。
Light Falloff
ライトからボリューメトリックフォグが広がっている距離です。
Falloff Function
ボリューメトリックフォグのフォールオフ関数です。
Light Core Size
ライトのホットスポットのサイズを増減します。
Ray March Step
ライトボリューム内をマーチする場合のステップサイズです。 値が小さいと、より細かい結果が作成されますが、計算時間が長くなります。
Planes ¶
Bump, Point Normal Planes in 2nd input
オンの場合、指定したすべての平面は入力2にあります。オフの場合は入力1です。
Bump, Point, Normal Name
該当する入力平面の名前。
Mask ¶
マスクを選択すれば、ノードの効果をマスクで定義した領域に制限することができます。マスクはマスク入力(サイド入力)または1番目の入力そのものから取得することができます。
Effect Amount
マスクが存在しない場合、一定量(0 = すべての入力、1 = すべての出力)により出力と入力を混合します。
マスクが存在する場合、この量によりマスクを乗算します。
Operation Mask
マスクとして使用するマスク平面をマスク入力から選択します。マスクの選択方法は下記のとおりです。
マスクには、ある平面や全体の平面のコンポーネントを指定することができます。 ベクトル平面をマスクとして用意した場合、そのコンポーネントは、画像のコンポーネントによって乗算されます。
Scalar Mask ('A', 'C.r')
C.r = I.r * M C.g = I.g * M C.b = I.b * M
Vector Mask ('C')
C.r = I.r * M.r C.g = I.g * M.g C.b = I.b * M.b
First Input
画像自体のアルファ平面への操作をマスクする場合に便利です。
Mask Input
サイドマスク入力からマスクを選択します。
Off
マスクをオフにします。マスク入力を切り離す必要はありません(マスクを一時的に無効にする場合に便利です)。
Resize Mask to Fit Image
マスク画像の解像度が出力画像と異なる場合、このパラメータをオンにすると、出力画像の解像度にマスクをスケールします。
このノードが断続的に変化していても、マスクが変化していない場合、Scale COPを配置すると、マスク画像のサイズ変更がやや速くなります。
これを行なわない場合は、このノードを処理する度に毎回スケールが発生します。
Invert Mask
マスクを反転し、完全に'マスクした'すべての部分がマスクのない状態になります。 これにより、マスクを使ったノードの後にInvert COPを挿入する必要がなくなります。
Scope ¶
Plane Scope
ColorのRGBコンポーネント、Alpha、および他の平面に対する範囲を指定します。 (C)RGBAマスクは、ColorコンポーネントとAlphaにのみ影響します。'C'は、すべてのRGBコンポーネントを切り替えます。
ColorとAlpha以外の平面の場合、平面の名前(適用可能な場合はコンポーネントも加えて)は、文字列フィールドで指定されます。 プルダウンメニューにより、このノードにある平面またはコンポーネントを選択できます。
平面は、その名前で設定されます。コンポーネントは、その平面とコンポーネントの名前の両方により指定されます。 '*'のワイルドカードによって、追加の平面をすべてスコープすることができます。平面やコンポーネントは、スペース区切りでいくつでも指定することができます。
例:
P N.x N.y P N Pz
Frame Scope ¶
Frame Scope
フレーム範囲で特定のフレームのスコーピングを可能にします。 これは、平面スコープに追加されます(したがって、あるフレームの平面は、修正を行なうスコープされたフレームと平面の両方である必要があります)。
All Frames
すべてのフレームがスコープされます。
Inside Range
サブ範囲の内側にあるすべてのフレームがスコープされます。
Outside Range
サブ範囲の外側にあるすべてのフレームがスコープされます。
Even Frames
偶数番号のフレームがスコープされます。
Odd Frames
奇数番号のフレームがスコープされます。
Specific Frames
ユーザ定義のフレームリストがスコープされます。
Frame Range
Inside/Outside Rangeの場合、このパラメータは、スコープする(またはスコープしない)シーケンスのサブ範囲を指定します。 これは、Timelineビューアモードで編集できます(ビューアの⌃ Ctrl + 2)
Frame Dropoff
Inside/Outside Rangeの場合、このパラメータは、前後の一定数のフレームを指定して、ゆっくりとスコープしたフレームまで増加させます。 この操作は、その入力とブレンドされ、多数のフレームに対してスコーピング効果を'イーズイン'または'イーズアウト'します。 これは、Timelineビューアモードで編集できます(ビューアの⌃ Ctrl + 2)
Non-scoped Effect
スコープされないフレームについて、入力画像と修正画像間のブレンド係数を設定します。 通常はゼロです(入力画像を使用)。ゼロ以外の値に設定すると、スコープされないフレームを'わずかに'スコープされないようにできます。 値は、0(スコープしない)から1(スコープする)の間で変化します。
Frame List
'Specific Frames(特定のフレーム)'のフレームリストです。フレーム番号はスペース区切りにしてください。
Automatically Adjust for Length Changes
シーケンス範囲が変化する場合、このパラメータを有効にすると、新しい範囲に合うようにサブ範囲とフレームドロップオフの長さが調整されます。
ローカル変数 ¶
L
シーケンス長さ。
S
シーケンスの開始。
E
シーケンスの終了。
IL
入力シーケンス長さ。
SR
シーケンスフレームレート。
NP
シーケンス内のフレームの数。
W,H
画像の幅と高さ。
I
画像のインデックス(開始フレームが0)。
IT
画像の時間(開始フレームが0)。
AI
現在の平面配列のインデックス。
PI
現在の平面インデックス。
PC
現在の平面内のチャンネルの数。
CXRES
Composite ProjectのX解像度。
CYRES
Composite ProjectのY解像度。
CPIXA
Composite Projectのピクセルアスペクト比。
CDEPTH
Composite Projectのラスター深度。
CBP
Composite Projectのブラックポイント。
CWP
Composite Projectのホワイトポイント。
Examples ¶
Lighting3d Example for Lighting compositing node
このサンプルでは、Lighting COPでディープラスターのポイントと法線の情報を使って、 3Dライティングをシミュレーションする方法を3通り(ポイントライティング、方向を持つ大気照明、法線なしのライティング)説明しています。

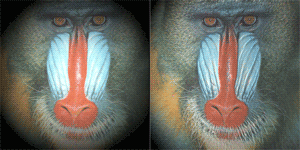
LightingFlatBump Example for Lighting compositing node
このサンプルでは、2D画像のLighting COPの効果を説明しています。 Flat LightingとバンプマップによるLightingのサンプルを載せています。
| See also |