| On this page | |
| Since | 18.0 |
Overview ¶
-
A UsdRenderSettings prim holds global render settings for rendering the scene, as well as a list of
UsdRenderProductprims representing the rendered files/buffers, and which purposes should be rendered. -
Render settings prims must be somewhere under
/Renderin the scene graph tree.
Creating vs. editing prims ¶
This node belongs to a class of nodes that create or edit USD prims directly. These nodes operate in Create mode_ or Edit mode_. This is controlled by a Create Primitives checkbox or an Action popup menu_. In Create mode, the node creates new prims. In Edit mode, the node changes the attributes on an existing prim. The Edit mode has two variations.
-
Edit will not modify primitives which have a
houdini:editableattribute set tofalse. -
Force Edit will modify a primitive regardless of the existence or value of this attribute. This attribute can be set on a primitive using the
Configure Primitives LOP.
Parameters that correspond to a USD attribute have a pop-up menu to the left that controls how the node authors the attribute. In addition to that, any connectable USD attributes (i.e., the ones in the inputs: namespace) will have menu items that allow disconnecting them from their sources.
Embree Robust option ¶
In some cases, strong light sources can create inconsistencies in the alpha channel in the form of black spots. The reason for the spots is that the Embree ray intersector is not 100% watertight and sometimes, rays can slip through between polygon edges. Then, a ray misses triangles where it actually hits them. This can, for example, occur with diced meshes. Higher samples per pixel can average out the spots and make alpha holes less perceptible. However, with matte holdouts (or any low-contrast regions) the variance oracle may shoot fewer rays and make the holes more noticeable.
As a workaround, you can create a custom paramater to expose the Embree Robust option for a more accurate intersection testing mode in Embree. Note that you might notice a slight decrease in performance when you turn on Embree Robust.
-
On the node’s Parameter editor, click the
Parameter Edit Menu. From the dropdown menu, choose Edit Parameter Interface. This choice opens a new panel with three columns (see screenshot below).
-
Go to the middle column and navigate to Karma ▸ Global ▸ Rendering.
-
Embree Robust will be a boolean toggle and you can use existing parameters as templates. Copy ⌃ Ctrl + C and paste (Ctrl + V) the two Cancel Render on No Working GPU Devices UI controls.
-
Rename the copied controls to
karma:global:embreerobust_controlandkarma:global:embreerobust. Make sure the Tags on the right column are set correctly. -
Click Accept to add the new toggles to the node’s parameter set.
-
Lay down a
Karma Render Settings LOP and connect its output with the input of the Render Settings Edit LOP.
-
On the Render Settings Edit LOP, let the Primitives parameter point to the Karma Render Settings LOP’s render settings in the Scene Graph Tree, for example
/Render/rendersettings. -
Turn on the new Embree Robust option.

If you want to verify that Embree Robust is turned on, go to the Scene Graph Tree and select the rendersettings entry. On the Scene Graph Details, you should now see a karma:global:embreerobust entry set to True.
Parameters ¶
Sampling Behavior
Cooking this node can generate many USD time samples, rather than just a single time sample at the current time. This can be equivalent to having a Cache LOP following this node, but it will evaluate much faster, and does not cache data from any other nodes. This allows animated data to be authored to USD without introducing a node time dependency which would then cause all following nodes to also be time dependent. This can vastly improve playback performance of some LOP Networks.
In all sampling modes, if a parameter on this node does not vary with time, and does not rely on other time sampled data from the stage, only a single default value will be generated in USD for the corresponding attribute. USD time samples are only generated for parameters that may vary over time.
Sample Current Frame
A single time sample will be generated for the current time.
Sample Frame Range If Input Is Not Time Dependent
If the input to this node is time dependent, this node behaves as if it is in Sample Current Frame mode. Otherwise it behaves as if it is in Sample Frame Range mode.
Sample Frame Range
The Start/End/Inc parameter is used to generate multiple times at which this node’s parameters are evaluated, and a USD time sample is created for each attribute at each one of these times.
Start/End/Inc
When the Sampling behavior is Sample Frame Range, this parameter controls the number and spacing of base time samples to be generated by this node. The default values of this parameter are @fstart, @fend, and @finc. These values correspond to the start, end, and step size of the global Houdini animation settings when interacting with Houdini. When using a ROP node to generate a range of frames, these values correspond to the start, end, and increment values specified on the ROP node being executed. This default ensures that a USD file written to disk will contain time samples for exactly the frame range requested by the ROP (regardless of the Houdini animation settings).
Subframe Sampling
For each primary sample generated by this node, these parameters can cause additional samples to be generated around that primary sample time. This is most often used to ensure that accurate data exists at exactly the camera shutter open and close times, as well as at the primary sample time.
Shutter
Controls the method used to specify the shutter open and close times relative to the primary sample times.
Specify Manually
The Shutter Open/Close parameter values provide exact offset values relative to the primary sample time.
Use Camera Prim
The Camera Prim parameter provides the scene graph path of a camera primitive from which the shutter open and close times are extracted to provide the offset values relative to the primary time sample.
Shutter Open/Close
When Shutter is set to Specify Manually, these two offset values are added to the primary sample time to indicate the shutter open and close times. The open time should be less than or equal to zero, and the close time should be greater than or equal to zero.
Camera Prim
When Shutter is set to Use Camera Prim, this is the scene graph path of a camera prim on the input node’s stage. The shutter open and close attribute values are read from this primitive.
Samples
The number of subframe samples to create for each primary sample. These samples are evenly distributed between the shutter open and close times. Note that such an even distribution may or may not create a sample at exactly the primary sample time.
Always Include Frame Sample
When turned on, forces a sample to be created at exactly the primary sample time. If the Samples value, together with the shutter open and close times, already place a sample at the primary sample time, turning on this option has no effect. Otherwise, this option causes an addition sample to be added. This means that the actual number of samples per primary sample may in fact be one more than the number specified in the Samples parameter.
Action
Whether this node should create new prims, or edit existing prims. In addition, the Force Edit option can be chosen to cause this node to ignore the houdini:editable attribute on prims, and always edit the specified attributes. This is in contrast to the Edit mode which will trigger a warning and not set attributes on prims with the houdini:editable attribute set to false.
Primitive Path
In Create mode, this lets you control where in the scene graph to create the prim(s).
The default is usually /$OS. This creates a primitive at the root level with the same name as the node (for example, /tube1). This is a useful default for preventing naming conflicts, but terrible for organization. You should try to remember to change the Primitive Path to a better value when you create prims.
For example, instead of naming models after the node that created them, you might want to name them after the geometry inside, and organize them under a /Models branch.
The Create Primitives section contains basic controls for how to create the new prim(s).
Primitives
In Edit mode, the node has a Primitive Pattern parameter. This lets you specify the prim(s) the node should operate on. You can click the select button beside the text box to select the primitives from the scene graph tree. You can also use primitive patterns for advanced matching, including matching all prims in a collection.
Initialize Parameters
Changes the state of all control menu parameters to Do Nothing, so that this node will not apply any changes. Also grabs the current values of each property from the first Primitives match, and sets the values of the corresponding parameters to match. This means that changing any parameter’s control menu to Set or Create mode will set the property to its current value, making it easier to apply changes to an existing value rather than setting a brand new value. With Rebuild Render-Specific Parameters you reset all parameters from render-specific tabs to their default values for the specific node. If you want to reset the parameters for the entire scene, you can also open the top-level Render menu and choose Rebuild All Render-Specific LOP Parameters.
This section only appears when the node is creating primitives.
For example:
-
If you want to create a new cube primitive at
/world/objects/cube1on an empty stage: Set Primitive Specifier to Define, and the Parent Primitive Type to Xform. -
If you want to override the radius of a sphere at
/world/objects/sphere1: Set Primitive Specifier to Over, and the Parent Primitive Type to None. This makes sure the primitive types of any existing ancestor prims are not be modified by this node.
Primitive Count
The number of primitives to create.
Primitive Type
Set all created prims to have this type.
Primitive Kind
Set all created prims to have this kind.
Primitive Specifier
The USD operator to use when creating the new prims.
Define
Authors a completely new prim. Use this if you want to create a brand new prim or replace an existing prim.
Over
Authors an override of an existing prim. Attributes not explicitly authored on this prim will get their values from the existing prim on the lower layer.
Class
Define a primitive class. This is usually not necessary unless you are doing deep USD magic.
Class Ancestor
If Primitive Specifier is Define or Over, this parameter will cause some ancestor primitives to be authored with a specifier of Class. This makes it easy to create an Over or Define within a Class without having to use two separate nodes. When Primitive Specifier is Class, this parameter is disabled because the entire primitive hierarchy is already authored as Class primitives.
Parent Primitive Type
If any parents of a path in Primitive Paths do not exist, this node will automatically create them. In this case, it will create parent nodes of this type.
Standard ¶
Ordered Products
A list of paths to UsdRenderProduct prims, representing the rendered outputs. If you don’t specify any explicit products, the renderer should by default output an RGB image using the render settings on this node, to a default display or image name.
Included Purposes
A list of purpose tokens (such as render (final render), proxy, and guide, from UsdGeomImageable). Only geometry with its purpose set to one of these tokens will be sent to the renderer. The default purpose is the purpose for all geometry that doesn’t have an explicitly set purpose, so you will usually want to include it.
(This cannot be specified per-product because it is a statement of which geometry is present.)
Material Binding Purposes
A list of material purpose tokens to consider when resolving material bindings.
Rendering Color Space
Describes a renderers working (linear) color space, where all the render/shader math is expected to happen. When no Rendering Color Space is provided, the renderer should us its own default.
Camera
Path to a USD camera (UsdGeomCamera) prim to render the scene from.
Resolution Mode
Use the USD Camera’s aperture aspect ratio to automatically set one dimension of the resolution.
The computed parm is set using an expression, but is locked to prevent accidental edits.
Manual
Set the resolution height and width values.
Set Width, Compute Height from Aperture
Set the width size, while height is computed from the width and the camera aspect ratio.
Set Height, Compute Width from Aperture
Set the height size, while width is computed from the width and the camera aspect ratio.
Resolution
The horizontal and vertical size of the output image, in pixels.
Disable Motion Blur
Turn off motion blur. This is equivalent to overriding the camera’s Shutter Close parameter to be equal to its Shutter Open time, to produce a zero-width shutter interval.
Disable Depth of Field
Turn off depth of field rendering. This is equivalent to overriding the camera’s F-Stop parameter to 0.0.
Aspect Ratio Conform Policy
What to do if the aspect ratio of the output image (Resolution width divided by height) doesn’t match the aspect ratio of the camera aperture (controlled by attributes on the camera). This allows a standard renderer to do something reasonable when you switch between cameras.
Expand Aperture
If necessary, expand the camera aperture to match the image.
Crop Aperture
If necessary, crop the camera aperture to match the image.
Adjust Aperture Width
If necessary, change the camera aperture width to match the image.
Adjust Aperture Height
If necessary, change the camera aperture height to match the image.
Adjust Pixel Aspect Ratio
Change the aspect ratio of the image to match the camera.
Data Window NDC
Directs the renderer to only render within this window of the entire output image. You specify the window as minX, minY, maxX, maxY, where each number is a normalized value from 0 to 1. 0, 0 is the bottom left, 1, 1 is the top right, 0.5, 0.5 is the center, and so on. The default is 0, 0, 1, 1 (no cropping). Note that you can use negative values. For example, -0.1, -0.1, 1.1, 1.1 will give you 10% overscan on each side.
You can use this window to temporarily crop the render to a smaller region, for testing purposes.
Pixels are only rendered if they are fully inside the window.
The normalized coordinates map to the image after any adjustments by the Aspect ratio conform policy.
Pixel Aspect Ratio
The aspect ratio (width/height) of image pixels (not the image itself).
The default is 1.0, indicating square pixels.
Karma ¶
Global ¶
Image Mode
Determines how the image will be rendered.
Progressive
The entire image will be progressively rendered, so the whole image resolves at the same time. This mode gives you a sense of what the whole image will look like without waiting for the render to complete.
Bucket
Each bucket renders to completion before advancing to the next bucket. This mode lets you see what the final quality will be like without waiting for the whole image to render.
Note
When rendering for IPR, Karma will use progressive rendering until the IPR preview passes are complete.
Progressive Passes
When rendering in Bucket mode (see Image Mode), this is the number of progressive passes over the image to perform before switching to bucket mode.
Bucket Size
Karma breaks down an image into multiple buckets for rendering. This is the side length (in pixels) of the square bucket. The default is 32, specifying a 32 pixel x 32 pixel bucket. Threads operate at the bucket level, so it might be useful to lower the bucket size if there are only a few buckets that are particularly expensive. That way the expensive areas can be divided across more threads.
For example, if the image is mostly empty, but there’s a distant object that fits within single 32 x 32 bucket, then that object will only be rendered using 1 thread. If you switch to a 16 x 16 bucket, then the object might be split across 4 buckets and have 4 threads working on it.
Ideally changing the bucket size doesn’t change the results, but Karma measures variance across pixels within the current bucket, so if you set it to a low value, for example 4, Karma only has 4 x 4 = 16 pixels to look at, so Karma will tend to make very poor variance estimates. This can show up as black pixels, where pixel rendering terminated prematurely due to a bad variance estimate.
Bucket Order
Specifies which buckets are rendered first. Values can be:
middle
Buckets start from the middle of the image.
top
Buckets at the top of the image are rendered first.
bottom
Buckets at the bottom of the image are rendered first.
left
Buckets at the left side of the image are rendered first.
right
Buckets at the right side of the image are rendered first.
Note: When rendering to MPlay, the user can click to focus on an area to render.
Cancel Render on No Working GPU Devices
Enabling this option will cause karma to stop the render with an error if no working GPU devices are discovered.
Export Components
A whitespace-separated list of shading component names that will be computed for export. If you have defined new component labels in your materials, these can be added to the list so that they are exported for per-component export planes. If you are not using some components, remove them from the list to improve render efficiency.
PBR light exports assume that this list is complete - that is, all components created by shaders are listed. If there are unlisted components, light exports may be missing illumination from these components.
Pixel Samples
The number of ray-samples sent through each pixel. More samples will result in a less noisy image. Also known as “primary samples”.
Path Traced Samples
The number of ray-samples sent through each pixel when using the path traced convergence mode. More samples will result in a less noisy image.
Screendoor Limit
The number of transparent samples to be shaded as a ray travels through partially opaque objects. Increasing this value will result in less noise in partially opaque objects and is generally less costly than increasing Pixel Samples, Volume Step Rate, or Min|Max Ray Samples. This parameter will not have any effect on noise from indirect sources however.
Convergence Mode
When set to Path Traced, a maximum of 1 indirect rays is generated per
bounce. When set to Automatic, the number of indirect rays is calculated
from an initial noise estimate, target noise threshold, and the maximum
number of camera rays. Also note that with Automatic, the number of
samples for direct lighting is adjusted based on noise estimate as well.
Russian Roulette Cutoff Depth
Depth at which indirect rays start to get stochastically pruned based on ray throughput.
Light Sampling Mode
Whether Karma should perform uniform sampling of lights or whether rendering should use the light tree. The light tree can be significantly faster for scenes that have large numbers of lights.
Some lights cannot be added to the light tree, and will all be sampled by Karma:
-
Dome Lights
-
Distant Lights
-
Point Lights
-
Lights with Light Filters
-
Lights with shaping controls (i.e. spot lights)
Light Sampling Quality
This is a global control to improve sampling quality for all lights. This acts as a multiplier on the individual light quality controls. Increasing the quality will improve direct light sampling as well as shadows/occlusion.
Image Blur
If you turn this off, Karma still calculates velocities, but sends all camera rays at shutter open, so the image will not have any apparent motion blur. This may be useful if you simply don’t want any motion blur. For example, if you want to add motion blur in post/compositing, but you still need the renderer to be aware of motion blur so that it saves out the proper motion vectors to an AOV.
Outlines
On/Off edge detection
Apply to Beauty
Apply lines to beauty, otherwise the result will be in outline AOV only.
Lines Types to AOVs
Output outline_contour, outline_crease, outline_depth lines types to separate AOVs.
Radius
defines a radius of the search, also could be interpreted as global lines thickness.
Primary
Primary rays edge detection on/off.
Primary Samples
Initial number of samples per stencil per each primary ray.
Primary Stencils
Active in outline_mode=0, increase number of stencil samples x2 with each new step-value per each primary ray.
Secondary Indirect
Reflection/refraction rays edge detection on/off.
Secondary Samples
Initial number of samples per stencil per each reflect/refract ray.
Secondary Stencils
Active in outline_mode=0, increase number of stencil samples x2 with each new step-value per each reflect/refract ray
Depth Threshold Scale
Global scale for Depth Threshold.
Intensity
Lines intensity.
Fit Min
Remapping outlines: min limit to fit.
Fit Max
Remapping outlines: max limit to fit.
Depth Blend
A float parameter which blends between two following modes:
-
0.0 - uniform across the z coordinate
-
1.0 - varying across the z coordinate
Modes
Two sampling modes provided: 0 - determined stencil samples pattern (less noisy) 1 - random stencil samples pattern
Default Color
Default color applied to outlines if there is export_outline_color AOV provided in the shader.
Debug
Output id, thickness, color outline data to export_outline_id, export_outline_thickness, export_outline_color AOVs.
Enable Indirect Guiding
When eabled, Karma collects radiance information on every shading point during the render and uses it to guide indirect bounce rays, rather than just relying on the BSDF sampling distribution. This can improve “difficult” lighting (for example, caustics, and mostly indirect lighting) but does add a bit of overhead. Before using this, you can try rendering direct and indirect AOVs to see where the noise is. If the noise is mostly caused by the direct lighting, there may be very little benefit.
Indirect Training Samples
The number of primary samples that karma will collect radiance information from. When set to 0, karma will collect information and refine guiding field throughout the entire render. If greater than zero, it will only do that until the specified number of samples and the remaining samples will be rendered using the guiding field but without refining it any further.
Indirect Guiding Components
List of BSDF components that use guiding for sampling when indirect guiding is enabled.
Indirect Guiding Deterministic
Attempts to produce deterministic result at increased render cost. Note that full determinism isn’t possible with multi-threaded renders since there may be tiny variations on geometry between runs (applies to any multi-threaded geometry processing such as precomputing normals, displacement, subdivision). This normally does not affect non-guided renders, but can cause butterfly effect with indirect guiding since the smallest variation may affect how the guiding field is built, which causes indirect rays to go in different directions, which leads to even more variation in the next iteration, and so on.
Indirect Guiding Render from Scratch Post-Training
Clears AOVs when training is completed for indirect guiding so that the pixel values accumulated during the training phase don’t contribute to the final render.
Ray Bias
The minimum distance used when testing if secondary rays from a surface intersect with other objects in the scene. The distance is measure from surface along the direction of the ray. Objects within the ray bias distance are ignored.
Automatic Ray Bias
Automatically compute ideal ray bias. Under Karma CPU, automatic bias applies to everything except procedural mesh and continued rays for partially opaque surfaces and nested dielectrics (the Ray Bias property is still used for those cases). Under Karma XPU, automatic bias applies to everything, but only for polymesh. For all other geometry types (eg points, curves) the Ray Bias property is still used.
Constrain by Maximum Roughness
Roughness parameter in GGX BSDFs are clamped by the maximum roughness value propagated down the ray chain in pathtracing. Enabling this option can cut out a lot of noise in indirect specular (in particular, cases where glossy surface is reflected by a rough specular surface) at the cost of a bit of accuracy.
Color Limit
The maximum value a shading sample is allowed to contribute to an LPE image plane to reduce appearance of “fireflies” caused by undersampling of extremely bright light sources. Note that reducing this value can result in an overall reduction in the amount of light in your scene.
Shared Color Limit
When enabled, indirect bounces use Color Limit value and Indirect Color Limit parameter is ignored.
Indirect Color Limit
Color limit applied to indirect bounce only. Note that this parameter is ignored unless Shared Color Limit toggle is disabled.
Automatic Headlight Creation
If there are no lights in the scene, a headlight is created by default. To
disable, turn off this checkbox. Note that this parameter is deprecated in
favor of Headlight mode in the USD Render ROP or the
--headlight command line argument in husk.
Background Holdouts Occlude Shadows
Prevent background holdouts from receiving shadows from non-holdouts if the shadow rays are occluded by background holdouts. Disabling this can be helpful in scenarios where the holdout mesh (and thus the cutout shape of the shadow) doesn’t match the shadows in the photo exactly, so you'd rather render out the whole shadow and roto out unwanted parts in comp.
Override Lighting
Override lighting in the scene. There are several options:
Off
Use the lighting as defined on the USD stage.
Emissive Objects
Disable all light sources so that only emissive objects (geometry lights) are enabled.
Headlight
Disable all light sources and create a headlight.
Dome Light
Disable all light sources and create a dome light.
Disable Lighting
Disable all lighting and material evaluation, using only the display color to shade primitives.
Headlight AO Samples
When rendering in Headlight mode, perform this many ambient occlusion samples per shade.
Headlight AO Distance
When rendering in Headlight mode with ambient occlusion shading, this distance is used for occlusion testing. Smaller values will result in faster, but less accurate shading.
Headlight Fog Color
The color of the depthcue fog for disabled lighting.
Headlight Fog Alpha
The alpha for depthcue fog when lighting is disabled.
Headlight Fog Distance
The near/far distance for depth cue fog when lighting is disabled. If the far distance is less than the near distance, fog will be disabled.
Dicing Camera
Specifies a camera that is used for dicing complicated surfaces. This can provide consistent dicing of surfaces when the viewing camera is moving.
Offscreen Quality
This parameter controls the shading quality scale factor for geometry that is not directly visible to the camera. For geometry that is outside the field of view (i.e. visible only to secondary rays), karma will smoothly reduce the shading quality based on the angle between the geometry and the edge of the viewing frustum. Smaller values can increase performance particularly in scenes where the camera is within the displacement bound of nearby geometry, where it permits the hidden primitives to be diced more coarsely than those that are directly visible.
Dicing Quality Scale
This parameter is a global multiplier for dicing quality of all objects.
Image Filters
Image filters post-process the filtered pixels to produce the final image. This parameter takes a string containing a JSON-encoded list of filters and their arguments. Usually you don’t need to craft this value by hand, it’s computed by the Karma LOP from the values of filter-related parameters. See Karma filters for more information.
Pixel Filter
Specifies the distribution of samples over pixels. A Box Filter will distribute samples randomly over the interior of each individual pixel. A Gaussian Filter will distribute samples in a disk around the pixel center, but with a Gaussian distribution (instead of a uniform distribution).
Pixel Filter Size
This is the size of the Pixel Filter. A Gaussian filter with a filter size
of 1.8 will be slightly less blurry than a Gaussian filter with a filter
size of 2.0.
Sample Filter
Sample filters are used to modify samples before they are sent to pixel filters.
This parameter specifies a list of filters. These filters are specified as a JSON list.
Pixel Oracle
When rendering, a Pixel Oracle tells Karma which pixels need additional sampling and which pixels are converged. This parameter tells karma which oracle to use.
uniform
Uniformly distribute rays to each pixel. Each pixel will always get the same number of ray-samples.
variance
Distribute rays based on variance in the rendered image.
Use Background
Off
Turns off Background IPR Filter.
Auto
Turns on Background IPR Filter only for IPR.
On
Turns on Background IPR Filter for both IPR and off-line rendering.
Background IPR Filter
JSON list of image filters specifically for background image preview and slap-comp of shadows and other holdout elements.
Export Components
A whitespace-separated list of shading component names that will be computed for export. If you have defined new component labels in your materials, these can be added to the list so that they are exported for per-component export planes. If you are not using some components, remove them from the list to improve render efficiency.
PBR light exports assume that this list is complete - that is, all components created by shaders are listed. If there are unlisted components, light exports may be missing illumination from these components.
DCM Use Hit Distance
When enabled, Z and Zback channels in deep EXR use distance to the camera instead of projected depth. This can be useful for deep compositing renders with custom lens shaders that do not use perspective projection (e.g. polar).
DCM Exclude Holdouts
Prevent holdouts from generating deep samples. This can be useful for deep holdout workflows where deep images are merged additively. Note that unlike flat images, holdout and non-holdout deep images cannot be produced within a single render (to avoid having to render twice, you could add holdout AOVs to deep product and disable this property to allow them to contribute as separate channels, but keep in mind when you do, you must flatten the deep image before adding holdout and non-holdout channels in comp).
IPR is the abbreviation for Interactive Photorealistic Rendering in the Solaris viewport when you turn on Karma CPU or Karma XPU. With IPR you get a fully rendered view of your scene that responds to any changes in perspective in real time. When the perspective no longer changes, the viewport rendering is increasingly refined until it reaches the adjusted number of samples.
Downsample Factor
When Karma starts rendering, it initially renders a low resolution image and scales it up for display. This parameter controls the amount of downsampling. A value of 1 produces higher quality initial images, but is also less interactive.
Denoise Bucket Size
This value is the number of downsample passes that are rendered before the denoise filter is applied on the image.
Reserve Threads
When rendering in the Solaris viewport, reserve this many threads for other Houdini tasks.
Continuous Dicing
For faster feedback, Karma will dice subdivision and displacement surfaces on the first render, but not if the camera tumbles. Continuous dicing will cause Karma to continually re-dice geometry when the view changes. This is more accurate, but less interactive.
Cache Limit
Whether to use a fixed size cache (karma:global:cachesize) or whether to use a proportion of physical memory (karma:global:cacheratio)
Cache Memory Ratio
The proportion of physical memory Karma will use for its unified cache.
For example, with the default vm_cacheratio of 0.25 and 16 GB of
physical memory, Karma will use 4 GB for its unified cache.
The unified cache stores dynamic, not loadable data used by the render including the following:
-
2D
.rattexture tiles -
3D
.i3dtexture tiles -
3D
.pcpoint cloud pages (when not preloaded into memory)
Note: This value is only used for off-line rendering, not IPR.
Cache Size (MB)
An explicit memory limit for the unified shading cache. This is deprecated in favor of using the Cache Memory Ratio.
Note: This value is only used for off-line rendering, not IPR.
Override Object Settings
Normally, geometry settings specified in the Render Settings LOP provide default values for objects. Each object can override the value of the default. With this parameter, the defaults specified on the Render Settings primitive will override the setting on every object.
This property changes the behavior of corresponding properties on the Default Geometry Settings. Those properties act as fallbacks in case no local values exist directly on the prims, but by providing property names to the Override Geometry Settings field, you can tell Karma to change the behavior from a fallback to an override, but only for those properties.
This parameter specifies a pattern of object property names whose values
will taken from the render settings, overriding any per-object settings.
For example, setting the pattern to diffuselimit will override the
diffuse limit for all objects with the value specified on the render
settings LOP.
You can use Houdini’s standard pattern matching syntax to override multiple properties at once. For example dicingdepth* would match dicingdepthmin and dicingdepthmax. An example for a more complicated pattern is dicingdepth*,fakecaustic*,^fakecausticsopacity.
Random Seed
This is the random seed to use for the render.
Cancel Render on Missing Texture
Enabling this option will cause karma to stop the render with an error if it encounters a missing texture map.
Diffuse Components
A space-separated list of component types that will behave like diffuse bounces. This will affect which reflection scope is used based on the ray type and also which bounce limit to use. Uncategorized component types are assumed to be reflections.
Refract Components
A space-separated list of component types that will behave like refract bounces. This will affect which reflection scope is used based on the ray type and also which bounce limit to use. Uncategorized component types are assumed to be reflections.
Volume Components
A space-separated list of component types that will behave like volume bounces. This will affect which reflection scope is used based on the ray type and also which bounce limit to use. Uncategorized component types are assumed to be reflections.
SSS Components
A space-separated list of component types that will behave like subsurface scatter bounces. This will affect which reflection scope is used based on the ray type and also which bounce limit to use. Not categorized component types are assumed to be reflections.
Map Type
Type of texture baking to do. Can choose between UDIM and PTex texture baking.
Object ID
Object ID for the object that will be unwrapped for texture baking. Texture baking will look for the objects in the scene that have the corresponding object ID per type (low resolution, cage and high resolution) and assigns them accordingly. There should only be one object per type
Tile
Tile number that this scene will be texture baking. For UDIM texture baking this is the UDIM index (between 1001 and 9999). For PTex texture baking, faces are laid out onto paginated grids ordered from largest to smallest area. The tile number refers to which page is being baked currently.
PTex Minimum Resolution
Minimum resolution of a single PTex face when doing PTex texture baking.
PTex Maximum Resolution
Maximum resolution of a single PTex face when doing PTex texture baking.
PTex Small Face Percent
Used with PTex Relative Scaling. Refers to how many quads should approximately have resolutions less than the minimum resolution in relative scaling. This value is only an estimate based on the approximate lengths/widths of each face.
PTex Relative Scaling
Used to enable relative scaling for PTex. Relative scaling attempts to adjust the resolution of the PTex faces rendered based on the size of the meshes and PTex Small Face Percent. Relative scaling will adjust the minimum resolution so that a percent of the faces have less resolution than this minimum. This percent is the PTex Small Face Percent.
PTex Scale
Used to adjust the scaling of PTex face resolutions when doing PTex baking.
Default Geometry Settings ¶
Enable Motion Blur
Whether to enable motion blur. Changing this in the display options will require a restart of the render.
Motion Samples from Stage
Instead of choosing the motion samples explicitly, Karma can also choose the motion samples based on the samples authored on the USD stage. This option will choose just the right number of samples to capture the motion described on the stage.
This setting applies to both transform and deformation motion samples for both geometry and instances.
Note
If the samples on the stage don’t align with the shutter times on the camera, it’s possible there will be some minor interpolation issues over the first and last segments (since motion will be truncated rather than interpolated).
Velocity Blur
This parameter lets you choose what type of geometry velocity blur to do on an object, if any. Separate from transform blur and deformation blur, you can render motion blur based on point movement, using attributes stored on the points that record change over time. You should use this type of blur if the number points in the geometry changes over time (for example, a particle simulation where points are born and die).
If your geometry changes topology frame-to-frame, Karma will not be able to interpolate the geometry to correctly calculate motion blur. In these cases, motion blur can use a velocities and/or accelerations attribute which is consistent even while the underlying geometry is changing. The surface of a fluid simulation is a good example of this. In this case, and other types of simulation data, the solvers will automatically create the velocity attribute.
Note
In Solaris, velocities, accelerations, and angularVelocities attributes are equivalent to v, accel, and w in SOPs, respectively.
No Velocity Blur
Do not render motion blur on this object, even if the renderer is set to allow motion blur.
Velocity Blur
To use velocity blur, you must compute and store point velocities in a point attribute velocities. The renderer uses this attribute, if it exists, to render velocity motion blur (assuming the renderer is set to allow motion blur). The velocities attribute may be created automatically by simulation nodes (such as particle DOPs), or you can compute and add it using the Point Velocity SOP.
The velocities attribute value is measured in Houdini units per second.
Acceleration Blur
To use acceleration blur, you must compute and store point acceleration in a point attribute accelerations. The renderer uses this attribute, if it exists, to render multi-segment acceleration motion blur (assuming the renderer is set to allow motion blur). The accel attribute may be created automatically by simulation nodes, or you can compute and add it using the Point Velocity SOP.
When Acceleration Blur is on, if the geometry has an angular velocity attribute (w), rapid rotation will also be blurred. This should be a vector attribute, where the components represent rotation speeds in radians per second around X, Y, and Z.
When this is set to Velocity Blur or Acceleration Blur, deformation blur is not applied to the object. When this is set to Acceleration Blur, use the Geometry Time Samples parameter to set the number of acceleration samples.

velocities) to do linear motion blur.
Geometry Time Samples
The number of sub-frame samples to compute when rendering deformation motion blur over the shutter open time. The default is 2 and this value is sufficient to properly blur rapidly deforming geometry. Note that Geometry Time Samples is limited by the number of sub-samples available in the USD file being rendered. An exception to this is the USDSkel deformer.
“Deformation” may refer to simple transformations at the Geometry/SOP level, or actual surface deformation, such as a character or object which changes shape rapidly over the course of a frame.
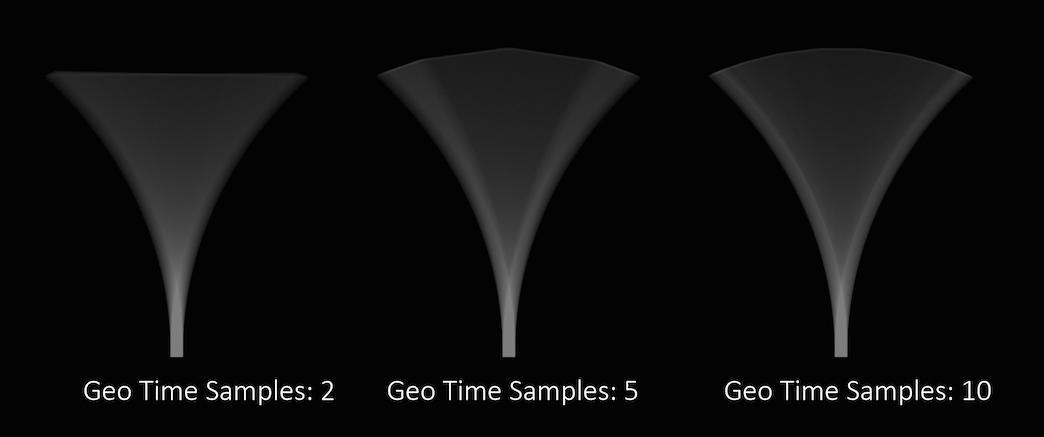
Objects whose deformations are quite complex within a single frame will require a higher number of Geo Time Samples.

Deformation blur also lets you blur attribute change over the shutter time. For example, if point colors are changing rapidly as the object moves, you can blur the Cd attribute.
Increasing the number of Geometry Time Samples can have an impact on the amount of memory Karma uses. For each additional sample, Karma must retain a copy of the geometry in memory while it samples across the shutter time. When optimizing your renders, it is a good idea to find the minimum number of Geometry Time Samples necessary to create a smooth motion trail.
Deformation blur is ignored for objects that have Velocity motion blur turned on.
For this parameter to override the samples on stage, you must also turn off the Motion Samples From Stage parameter.
Note that specifying the number of samples with this parameter may cause Karma to interpolate data from the samples written on the stage. It’s recommended that you simply use the Motion Samples from Stage setting to let Karma use the data that’s available. This setting may be required if you're using acceleration blur.
Transform Time Samples
The number of samples to compute when rendering transformation motion blur over the shutter open time. The default is 2 samples (at the start and end of the shutter time), giving one blurred segment.

If you have objects moving and changing direction extremely quickly, you might want to increase the number of samples to capture the sub-frame direction changes.
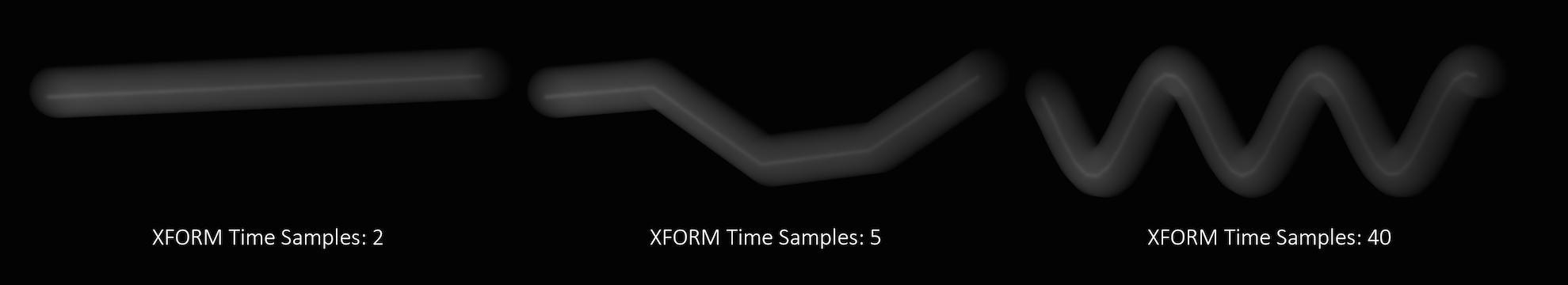
In the above example, it requires 40 transformation samples to correctly render the complex motion that occurs within one frame. (This amount of change within a single frame is very unusual and only used as a demonstration.)
Transformation blur simulates blur by interpolating each object’s transformation between frames, so it’s cheap to compute but does not capture surface deformation. To enable blurring deforming geometry, increase karma:object:geosamples.
For this parameter to override the samples on stage, you must also turn off the Motion Samples From Stage parameter.
Note that specifying the number of samples with this parameter may cause Karma to interpolate data from the samples written on the stage. It’s recommended that you simply use the Motion Samples from Stage setting to let Karma use the data that’s available.
Motion Blur Style
Specifies the style of motion the object has.
Rotation Blur (default)
Rotates the object around the origin. This is ideal for objects that spin.
Linear Blur
This style of motion will not preserve the volume of rotating objects and will have linear motion instead of rotational arcs. Should only be used in special cases, i.e. with pivot transformations. Linear blur linearly interpolates the coefficients of the transformation matrix to achieve a correct blur.
Instance Velocity Blur
When defining motion blur on instances, the transform of each instance can be blurred in addition to any motion blur occurring on the prototype. This option controls how the instance will compute the motion blur of the transform on each instance. For example, when instancing prototypes to a particle system, you'd likely want to use velocity blur to compute motion blur (the transform on the prototype would be blurred by the velocity on the particles).
No Velocity Blur
Use deformation blur of the instance to compute the blur on the transform.
Velocity Blur
To use velocity blur, the instance must be a point instancer with a velocities attributes on the points, or a native instance with a v primvar.
The velocities attribute (or v primvar) value is measured in Houdini units per second.
Acceleration Blur
To use acceleration blur, the instance must be a point instancer with point velocities and acceleration values. The renderer uses this attribute, if it exists, to render multi-segment acceleration motion blur (assuming the renderer is set to allow motion blur). The accel attribute may be created automatically by simulation nodes, or you can compute and add it using the Point Velocity SOP; this will be converted to
accelerations when the SOP geometry is converted to USD.
Instance Motion Samples
When motion blur on instances is computed using Acceleration Blur or Deformation Blur, this parameter specifies the number of motion segments used for motion blur.
Volume Velocity Blur Mode
Choose velocity blur method for volumes.
Lattice Deformation
Motion sampled via a deforming superstructure.
Lookup Offset
Sample coordinate is offset by velocity field value.
Note
Lattice Deformation mode can produce results with higher quality and handle cases such as disparate features of a volume overlapping post-blur. Lookup Offset mode can be more performant, particularly with reduced-resolution velocity fields. However, this mode is more prone to clipping issues if the sampled position is outside the bounds of velocity field. There, the lattice doesn’t have velocity information.
Volume Velocity Blur Scale
Velocity multiplier used to reduce or exaggerate amount of motion blur on volumes.
Volume Velocity Lattice Quality
Controls the resolution of the lattice super structure that is used for volume motion blur. Values closer to 1 result in a structure with velocities closer to the original velocity data, but longer render time.
Diffuse Quality
This parameter acts as a multiplier on Min Secondary Samples and Max Secondary Samples for indirect diffuse component.
Reflection Quality
This parameter acts as a multiplier on Min Secondary Samples and Max Secondary Samples for indirect reflect component.
Refraction Quality
This parameter acts as a multiplier on Min Secondary Samples and Max Secondary Samples for indirect refract component.
Volume Quality
This parameter acts as a multiplier on Min Secondary Samples and Max Secondary Samples for indirect volume component.
SSS Quality
This parameter acts as a multiplier on Min Secondary Samples and Max Secondary Samples for SSS component.
Volume Step Rate
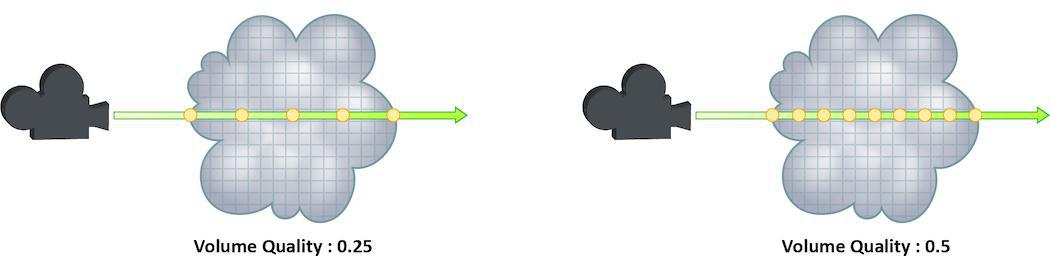
How finely or coarsely a volume is sampled as a ray travels through it. Volumetric objects are made up of 3D structures called Voxels, the value of this parameter represents the number of voxels a ray will travel through before performing another sample.
The default value is 0.25, which means that every one of every four
voxels will be sampled. A value of 1 would mean that all voxels are
sampled and a value of 2 would mean that all voxels are sampled twice. This
means that the volume step rate value behaves in a similar way to pixel
samples, acting as a multiplier on the total number of samples for
volumetric objects.
Keep in mind that increasing the volume step rate can dramatically increase
render times, so it should only be adjusted when necessary. Also, while
increasing the default from 0.25 can reduce volumetric noise, increasing
the value beyond 1 will rarely see similar results.
Volume Shadow Step Rate
A factor to proportionally decrease the volume step rate only for shadows,
relative to the volume step rate. Smaller values will cause Karma to use a
larger ray march step size for shadow rays than other shading rays. A
value of 1 will produce equal quality for shadow rays and shading rays.
Volume Sampling Field
Specifies the volume field by name that will be used for empty space culling. By default Karma will use the 'density' field if it exists. If you are rendering an emissive volume in which some parts of the volume have a 0 density, but still need to be rendered, you should specify a different field using this parameter.
Volume Filter
Some volume primitives can use a filter during evaluation of volume
channels. This specifies the filter. The default box filter is fast to
evaluate and produces sharp renders for most smooth fluid simulations. If
your voxel data contains aliasing (stairstepping along edges), you may need
to use a larger filter width or smoother filter to produce acceptable
results. For aliased volume data, gauss is a good filter with a filter
width of 1.5.
-
point -
box -
gauss -
bartlett -
blackman -
catrom -
hanning -
mitchell
Volume Filter Width
This specifies the filter width for the Volume Filter property. The filter width is specified in number of voxels. Larger filter widths take longer to render and produce blurrier renders, but may be necessary to combat aliasing in some kinds of voxel data.
Secondary Noise Level
Noise threshold to determine the number of indirect rays cast for indirect bounce when the Convergence Mode is set to Automatic. Decreasing this threshold (for example, to 0.001) will theoretically send more indirect rays and decrease noise, however the “extra” rays will likely be cancelled out by the Max Ray Samples parameter. The correct way to decrease noise is to increase the number of samples per pixel, rather than change this threshold.
If you are using Variance Pixel Oracle, you should set the same value for both threshold parameters. Setting the oracle’s threshold lower may make the indirect component reach its threshold sooner and cast fewer indirect rays, but the oracle decides to cast more expensive camera rays because the amount of final noise in the beauty pass is higher than the oracle’s threshold.
Min Secondary Samples
Minimum number of rays to cast in per-component variance anti-aliasing.
Max Secondary Samples
Maximum number of rays to cast in per-component variance anti-aliasing.
Diffuse Limit
The number of times diffuse rays can propagate through your scene.
Unlike the Reflection Limit and Refraction Limit, this parameter will increase the overall amount of light in your scene and contribute to the majority of global illumination. With this parameter set above zero diffuse surfaces will accumulate light from other objects in addition to direct light sources.



In this example, increasing the Diffuse Limit has a dramatic effect on the appearance of the final image. To replicate realistic lighting conditions, it is often necessary to increase the Diffuse Limit. However, since the amount of light contribution usually decreases with each diffuse bounce, increasing the _Diffuse Limit beyond 4 does little to improve the visual fidelity of a scene. Additionally, increasing the Diffuse Limit can dramatically increase noise levels and render times.
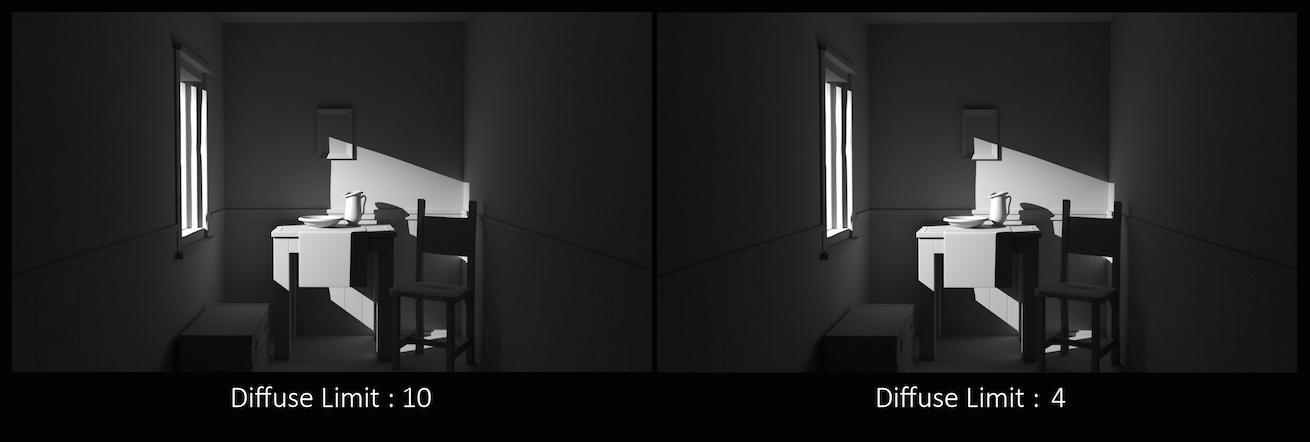

This is a float because all limits are stochastically picked per-sample, so for example you can set the diffuse limit to 3.25 and have 25% of the rays with a diffuse limit of 4 and 75% of rays with a diffuse limit of 3.
Reflection Limit
The number of times a ray can be reflected in your scene.
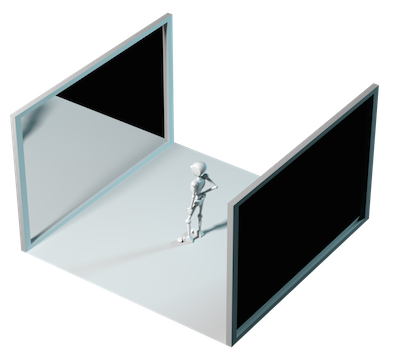
This example shows a classic “Hall of Mirrors” scenario with the subject placed between two mirrors.
This effectively creates an infinite series of reflections.
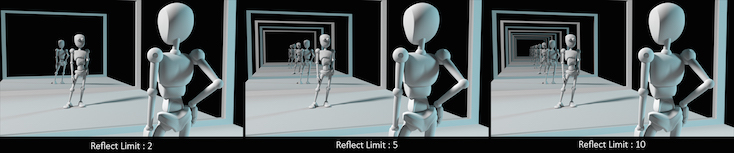
Remember that the first time a light source is reflected in an object, it is considered a direct reflection. Therefore, even with Reflection Limit set to 0, you will still see specular reflections of light sources.



From this camera angle the reflection limits are very obvious and have a large impact on the accuracy of the final image. However, in most cases the reflection limit will be more subtle, allowing you to reduce the number of reflections in your scene and optimize the time it takes to render them.
This is a float because all limits are stochastically picked per-sample, so for example you can set the diffuse limit to 3.25 and have 25% of the rays with a diffuse limit of 4 and 75% of rays with a diffuse limit of 3.
Refraction Limit
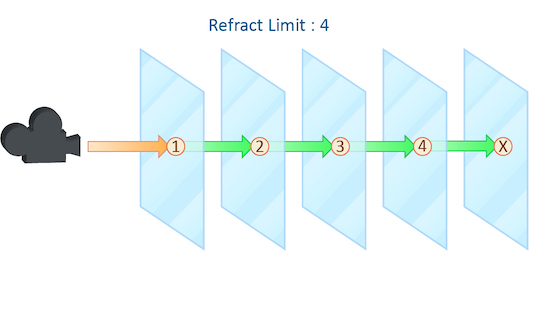
This parameter control the number of times a ray be refracted in your scene.
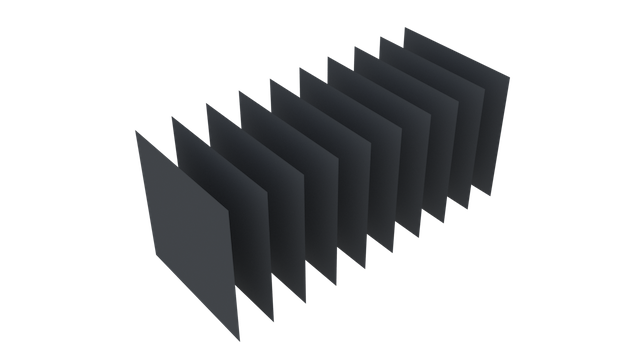
This example shows a simple scene with ten grids all in a row.

By applying a refractive shader, we will be able see through the grids to an image of a sunset in the background.
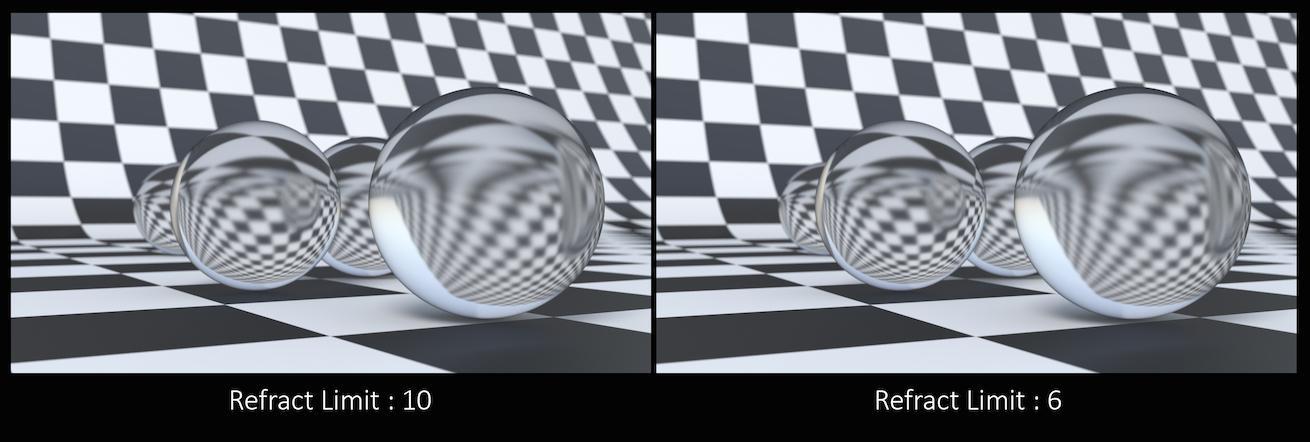
From this camera angle, in order for the image to be accurate, the refraction limit must match the number of grids that that are in the scene. However, most scenes will not have this number of refractive objects all in a row and so it is possible to reduce the refract limit without affecting the final image while also reducing the time it takes to render them.
Keep in mind that this Refraction Limit refers to the number of surfaces that the ray must travel through, not the number of objects.
Remember that the first time a light source is refracted through a surface, it is considered a direct refraction. Therefore, even with __Refraction Limit___ set to 0, you will see refractions of light sources. However, since most objects in your scene will have at least two surfaces between it and the light source, direct refractions are often not evident in your final render.
This is a float because all limits are stochastically picked per-sample, so for example you can set the diffuse limit to 3.25 and have 25% of the rays with a diffuse limit of 4 and 75% of rays with a diffuse limit of 3.
Volume Limit
The number of times a volumetric ray can propagate through a scene. It functions in a similar fashion to the Diffuse Limit parameter.
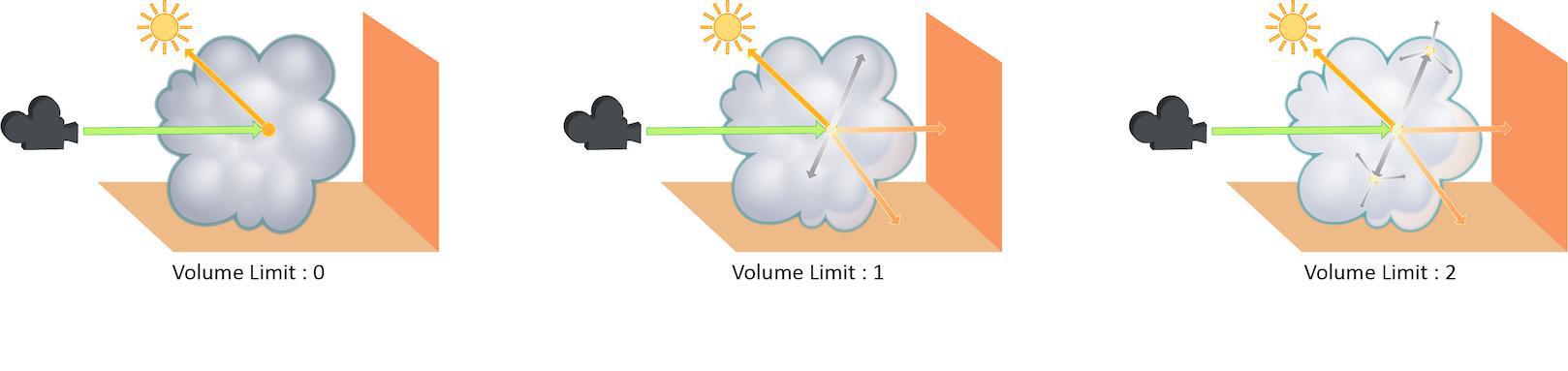
Increasing the Volume Limit parameter will result in much more realistic volumetric effects. This is especially noticeable in situations where only part of a volume is receiving direct lighting. Also, in order for a volumetric object to receive indirect light from other objects, the Volume Limit parameter must be set above 0.

With the Volume Limit set to values above zero, the fog volume takes on the characteristic light scattering you would expect from light traveling through a volume. However, as with the Diffuse Limit, the light contribution generally decreases with each bounced ray and therefore using values above 4 does not necessarily result in a noticeably more realistic image.
Also, increasing the value of this parameter can dramatically increase the amount of time spent rendering volumetric images.
This is a float because all limits are stochastically picked per-sample, so for example you can set the diffuse limit to 3.25 and have 25% of the rays with a diffuse limit of 4 and 75% of rays with a diffuse limit of 3.
SSS Limit
The number of times a SSS ray can propagate through a scene. It functions in a similar fashion to the Diffuse Limit parameter.
This is a float because all limits are stochastically picked per-sample, so for example you can set the diffuse limit to 3.25 and have 25% of the rays with a diffuse limit of 4 and 75% of rays with a diffuse limit of 3.
Limit Components
The ray types that the bounce limit color is applied to.
Limit Color
The color that will be used when a specific ray type reaches the limit.
Uniform Volume
Whether to render this object as if it was a uniform-density volume. Using this property on surface geometry is more efficient than actually creating a volume object of uniform density, since the renderer can assume that the volume density is uniform and place samples more optimally. The surface normal of the surface is used to determine which side of the surface will render as a volume - the normal will point away from the interior. The surface need not be closed - if the surface is not closed, the volume will extend an infinite distance away from the surface. Non-closed surfaces may produce unexpected results near the edge of the surface, so try to keep the viewing camera away from the edges.
Uniform Volume Samples
The number of samples to generate when rendering a uniform volume
(karma:object:volumeuniform is enabled). The samples will be distributed
so as to produce an equal image contribution if they were all equal in
brightness. Note that this property has no effect when global Screendoor
Limit is greater than 0, so for all practical purposes it is deprecated.
Render Visibility
Controls the visibility of an object to different types of rays using a category expression. This parameter generalizes the Phantom and Renderable toggles and allows more specific control over the visibility of an object to the different ray types supported by karma and VEX.
|
Rays sent from the camera |
|
Shadow rays |
|
Diffuse rays |
|
Reflections |
|
Refractions |
For example, to create a phantom object, set the expression to -primary. To create an unrenderable object, set the expression to an empty string . These tokens correspond to the string given to “raystyle” in the VEX trace() and gather() functions.
Stencil Map
This map type controls polygon visibility without invoking the shading engine. This means that you typically don’t need an opacity map on the shader/material. The stencil map uses the default texture coordinates (st) to do a quick unfiltered texture evaluation. By default, any pixel with a value of 0 makes the polygon invisible to any rays. However, you can change this limit with Stencil Threshold.
Stencil Threshold
Pixels with values less than or equal to this threshold will be invisibles to rays.
Cusp Angle
If there are no normals on an object, any edges with a dihedral angle greater than this value will be cusped. For compatibility with Mantra, Karma will also look for a detail attribute named vm_cuspangle (which takes priority over the setting).
Holdout Mode
When this is set to Matte mode, the object will be considered to be a cutout matte. Any lighting contribution and alpha of the object will be redirected to LPE AOVs with “holdouts” prefix. Holdout Mode does not affect the utility AOVs such as ray:hitP and ray:hitN.
Background mode is similar to Matte, except it’s used for background plate so it will appear “pre-lit” in indirect bounces, multiplied by shadow contribution. Diffuse albedo of the shader is used to determine the pre-lit irradiance.
Fix Shadow Terminator
Adjust shading position of shadow rays to avoid self-shadowing artifacts on low-poly meshes due to the discrepancy between smooth normals and face normals.
Custom Tracesets
A space-separated list of custom traceset names. You can use tracesets to subdivide a mesh into different parts, i.e. in conjunction with the Karma Texture Baker LOP. For example, the clothing on a character might have tracesets like
pants, shirt and jacket. On the Karma Texture Baker LOP’s Bake Traceset parameter you can then define which part/traceset you want to bake.
LPE Tag
Custom label assigned to lights or objects for use with Light Path Expressions.
SSS Traceset
Custom traceset for random walk subsurface scatter. Without a traceset, random walk will only trace against itself. With a traceset, it will trace against every geometry in the scene that shares the same traceset name.
Note
With instancing, this property must be defined on the prototype. Per-instance tracesets are not supported.
Enable Internal Reflection
Lets you evaluate the internal reflection on the backface of a glossy transmissive BSDF. Turn on this option to apply internal reflections. Note that this option has no effect on MaterialX Standard Surfaces with Thin Walled turned on: these materials always show internal reflections.
Internal reflections can cause black areas on an object’s back faces due to a loss of energy. To avoid this, turn off Enable Internal Reflection.
Thinwall at Refract Limit
Paths can become trapped inside refractive objects due to total internal reflection, hitting the refract/reflect limits and causing dark artifacts. Thinwall At Refract Limit treats surfaces as “thin walled” once these limits are reached, allowing further hits to pass through without bending or reflecting. This helps paths escape refractive objects without needing high refract/reflect limits (improving both look and performance).
Direct Refraction Subset
For compound BSDFs with refractive components, only apply direct lighting for lights that belong in specified location. A light ray facing the same direction as geometry normal is considered Outside. For transparent material that are solid/closed-manifold, setting this parameter to Outside can improve render performance by reducing noise in direct lighting and cut down on wasted shadow rays.
Dielectric Priority
Specifies the priority of a refractive material, allowing the renderer to
choose which of many overlapping refractive materials should take precedence
while rendering. This enables effects like water in a glass with ice cubes.
The default (highest priority) is 0, and as the number increases (1, 2, 3, etc.), the priority decreases.
Bump Shadow Terminator
Softens harsh shadow transitions from strong bump or normal maps. The shadow terminator is smoothly blended up to the specified threshold (in radians). A value of 0 disables the effect.
Enable Caustics
Brute-force caustics from transmissive objects. Allows evaluation of glossy BSDF that’s seen by indirect diffuse bounce. Often requires a significantly higher number of diffuse rays to resolve, especially if Roughness Clamp parameter is set to very small value or Indirect Guiding feature is disabled.
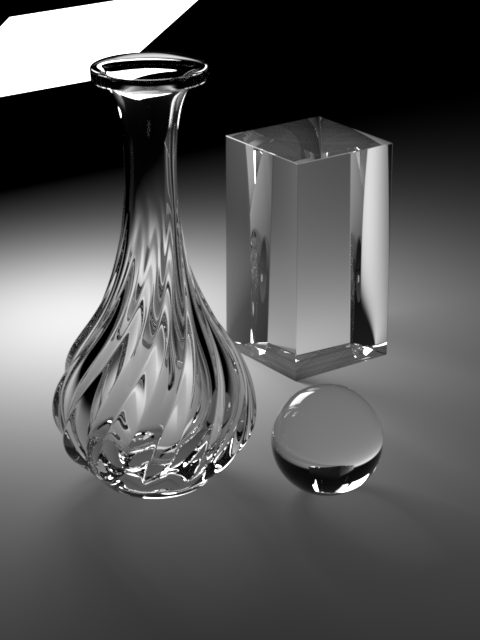
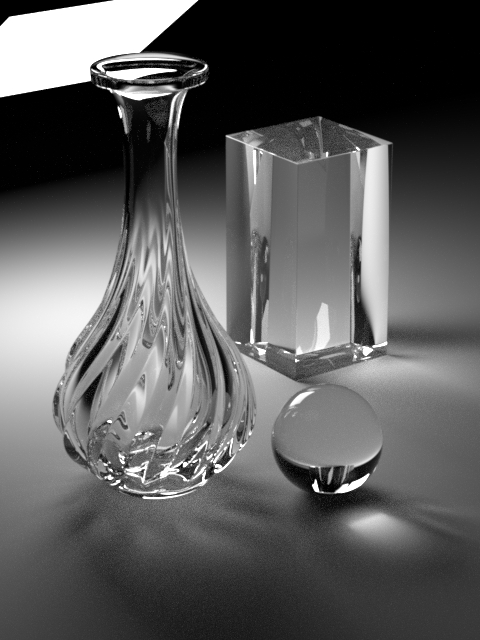


Roughness Clamp
Forces a minimal roughness for true caustics, above what the shader has set. Increasing this value can make caustics less noisy at the cost of accuracy.
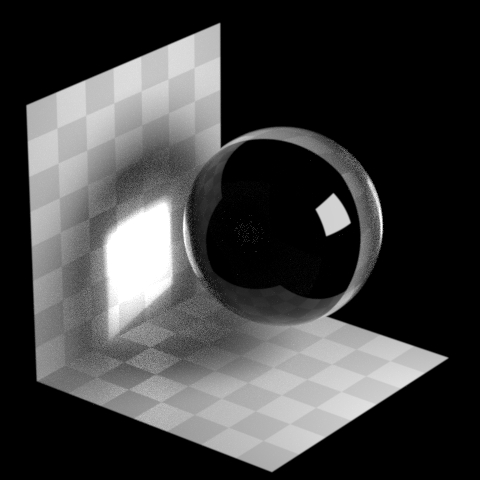
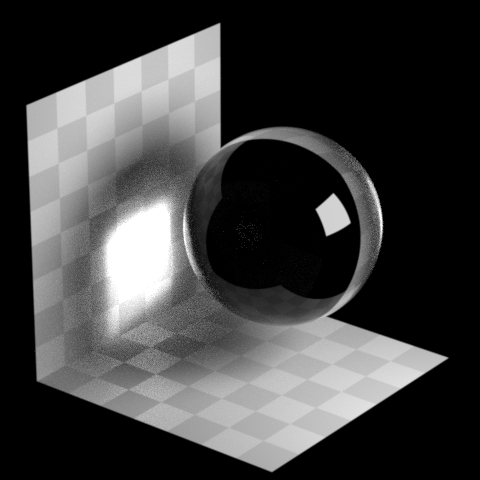
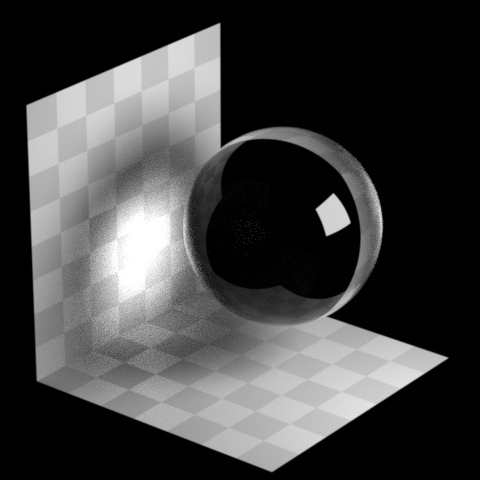
Note
Roughness clamp only works with GGX BSDF and may not have any effect with Phong, cone, or specular BSDFs.
Evaluate BSDF on Fake Caustics
Allows the BSDF to affect the fake caustics, meaning that, for example, a red bottle will automatically cast red shadows. Disabling the BSDF can reduce render times, but means Color should be used instead to set a constant shadow color.
Color
Tints the fake caustics. Use this to darken the result of the BDSF, or to set a constant shadow color if the BSDF is disabled.
Opacity
Controls the opacity of fake caustics. Use this to lighten the result of the BDSF.
Fresnel Darken
Controls the darkening of the Fresnel effect on the fake caustics shadow. A value of 0 turns the feature off and value of 1 fully darkens the shadow.
Efficient Emissive Sampling
Any object with an emissive material will generate light within the scene. If an object is significant enough (e.g. size, brightness, etc…) then it is possible for Karma to treat that object as if it were an explicit light source (similar to regular lights), meaning the emitted light will be handled much more efficiently. But doing so will add extra overhead elsewhere in the system (e.g. increased memory usage, slower update times, etc…).
There are three options. No will set the object as not being a light source. Yes will set the object as being a light source. Auto (default) means Karma will use an internal heuristic to decide if the object should be treated as a light source.
Is Portal
When enabled, the object will turn into a “light portal” that only lets in certain portion of dome lights based on portal geometry visibility.
Portal Dome Lights
Space-separated list of dome lights to associate this portal with.
Render Points As
When rendering point clouds, they can be rendered as camera oriented discs, spheres or discs oriented to the normal attribute.
Render Curves As
When rendering curves, they can be rendered as ribbons oriented to face the camera, rounded tubes or ribbons oriented to the normal attribute attached to the points.
Note that, due to a technical limitation, Karma CPU can’t render linear curves as oriented ribbons. In this case, go to the import LOP that loads the curve and turn on Geometry Handling ▸ Treat Polygons as Subdivision Surfaces. This option will import the curves as B-Splines.
Override Curves Basis
USD supports Curve Basis types that may not be supported directly in Houdini. In some cases, you may want to override the Houdini curve basis. For example, if you have linear curves in Houdini, you may want to render them with a Bezier, B-Spline or Catmull-Rom basis. This menu will force Karma to override the basis that’s tied to the USD primitives.
Note that the topology of the curves must match the target basis. For
example, when selecting any cubic curve basis, every curves must have at
least four vertices. For the Bezier basis, curves must have 4 + 3*N vertices.
Width Scale
A uniform scale applied to point and curve widths. This can be used to adjust the size of points and the radius of curves without having to modify the geometry.
Cull Backface
If enabled, geometry that are facing away from the camera are not rendered.
Dicing Quality
This parameter controls the geometric subdivision resolution for smooth surfaces (subdivision surfaces and displaced surfaces). With all other parameters at their defaults, a value of 1 means that approximately one micropolygon will be created per pixel. A higher value will generate smaller micropolygons meaning that more shading will occur - but the quality will be higher.
The effect of changing the shading quality is to increase or decrease the amount of shading by a factor of karma:object:dicingquality squared - so a shading quality of 2 will perform four times as much shading. A shading quality of 0.5 will perform 1/4 times as much shading.
True Displacements
This setting controls how the displacement shader on the object will be run.
Bump Mapped Displacement
The displacement shader is run, but only modifies the surface normal. This does not dice geometry and can save memory. With Karma XPU, this option only works in conjunction with float-based displacement maps. Also make sure to set the MtlX Image VOP’s Signature drop down menu to Float. Vector-based displacement maps are not supported in Karma XPU with this mode turned on.
Please also note that this mode generally doesn’t work with Karma XPU when you mix two or more MtlX Standard Surface VOPs.
True Displacement
The geometry is diced and displaced. This will cause proper silhouettes and shadowing of displaced surfaces.
Disable Displacement Shader
Disable the displacement shader entirely. There will be no bump mapping or displaced geometry.
Dicing Minimum Depth
When not set to -1, Karma will set minimum number of rows and columns on each face to be 2 to the power of this value when dicing for subdivision or displacement.
Dicing Maximum Depth
When not set to -1, Karma will set maximum number of rows and columns on each face to be 2 to the power of this value when dicing for subdivision or displacement. Setting the same (or lower) value as Dicing Minimum Depth is effectively equivalent to fixed parametric subdivision that ignores raster space/offscreen measurement. Recommended leaving this value at -1.
Dicing Predisplace
Enable this to apply trial displacement prior to dicing for improved raster space measurement. This helps avoid undertessellation with extreme displacements or when offscreen geometry is supposed to enter camera frustum post-displacement.
Low Resolution Object ID
Defines this object as the low resolution object corresponding to said Texture Baking Object ID. This means that the texture space of this object is what is being baked. If no high resolution object exists for this Object ID, this is the rendered appearance for the texture in that space as well. This is required for texture baking.
Cage Object ID
Defines this object as the cage object corresponding to said Texture Baking Object ID. This means that this object is used to help resolve normal discontinuities during texture baking of the low resolution object. This is optional for texture baking.
High Resolution Object ID
Defines this object as the high resolution object corresponding to said Texture Baking Object ID. This means that the rendered appearance of this object is what is being baked into the texture space the low resolution object. This is optional for texture baking.
Identifier Traceset
The name of the traceset on the high resolution object. A bake_traceset string primvar is also required on the low resolution object. When both, Identifier Traceset name and primvar, match, the object will be visible to primary rays.
Visibility Traceset
The traceset that is defined through Identifier Traceset. When availavle, it indicates which objects are visible to secondary rays, for example ambient occlusion, curvature, thickness, cavity, etc.
Visibility Cull Backface
If enabled, geometry that are facing away from the secondary ray (Ao, Cu, Cv, Th, etc.) are not intersected.
Enable
Per object lines on/off.
Radius
Controls outline thickness. Arctangent of this parameter determines the cone angle to cast stencil rays to do edge detection. It will be multiplied by karma:global:outline_radius.
Contour
Contour detection on/off. Contour lines are based on automatically assigned object id if
export_outline_id is not provided as a value or texture (as shader export).
Id Threshold
Threshold which estimates how different is id values of the main ray and stencil ray.
Crease
Crease lines for hard surfaces on/off.
Crease Threshold
Threshold which estimates how N direction changes in the area of stencil radius.
Depth
Depth lines on/off.
Depth Threshold
Threshold which estimates how z-depth values changes in the area of stencil radius.
Secondary
Indirect lines on/off.
Husk ¶
Default Delegate
Specify the default render delegate that husk should use when rendering using this render settings primitive.
The --renderer command line argument overrides this value.
If the value is empty, the value of the HOUDINI_HUSK_DEFAULT_DELEGATE environment variable is used.
If multiple render settings are rendered in a single husk process, the first render settings primitive will be used to determine the default delegate.