| Since | 21.0 |
This component sets up spine controls for a character. It can be run in a loop over different segments, or parts, of a character.
The spine component sets up a tangent spline with 4 controls - the root control, root CV (control vertex), tip CV, and tip control. The COG control, mid control, and end control allow you to further translate and rotate the spine, with the COG control being the main parent of the spine:
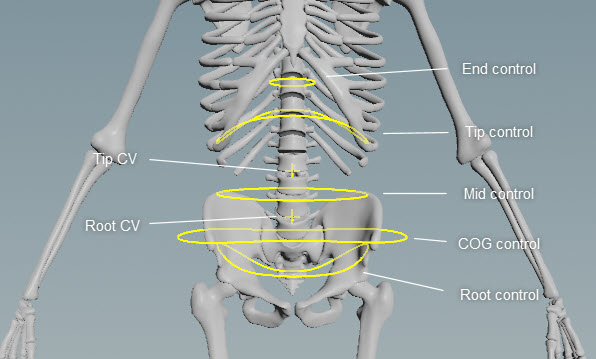
By default, the CVs are parented to the closest outer spline control, so the root CV is parented to the root control, and the tip CV is parented to the tip control:
In the viewport, the menu provides configuration options for the spine component. To stretch the spine, turn on the Add Stretch Control parameter in the Settings tab. This adds a slider configuration parameter to the
menu that allows you to adjust the stretch of the spine (see the gear menu for descriptions of the different types of interaction elements):
This component is very similar to the spline rig component. See rigging a character for an example use of the spline component.
Parameters ¶
Name
The name to add to the nodes created by this component. When using Segments, the segment name is also added to the node names.
Settings ¶
Type
The type of spline curve to create from the control points.
Curve Order
The number of control points used to construct the curve. By default, Curve Order is set to 4 because we have the following control points for the spline - the root control, root CV, tip CV, and tip control (see the parameters in the Driver tab).
A Bezier curve (the curve type is set in parameter Type) requires that the number of control points is equal to the curve order. Compound curves share a control point between their individual curve segments, so each additional curve segment requires an additional order-1 control points. This requirement can be expressed by the equation <number_of_control_points> % (order-1) == 1. See control spline for more information.
Pin Root
When turned on, constrains the orientation of the root joint to the root control (the root joint is the joint driven by the root control).
Pin Tip
When turned on, constrains the orientation of the tip joint to the tip control (the tip joint is the joint driven by the tip control).
Add Stretch Control
When turned on, adds a slider configuration parameter in the spine component’s menu that allows you to adjust the stretch of the spine:
Stretch
Specifies whether to keep the length of the spine. When set to 0, the spine keeps its length. When set to 1, the spine stretches to follow the control point.
Stretch Scale
Controls the amount of stretch. Increasing this value increases the effect of the stretch.
Squash Scale
Controls the amount of squash. Increasing this value increases the effect of the squash.
Keep Tip Scale
When turned on, the scaling at the tip of the spine remains unchanged as you stretch the spine. When turned off, the tip of the spine is scaled as you stretch the spine.
Note
You can only see the effects of the scaling if Stretch Scale or Squash Scale is greater than 1.
Driven ¶
Segments
Segments are tags that separate each spine chain. Tags can be set up on skeleton joints using an Attribute Adjust Array SOP. See preparing skeletons for rigging for more information.
If Segments is empty, the spine logic is run once.
Note
The Segments parameter does not take APEX path patterns, for example, the #<tag> function. Instead, specify the tag names directly in this field.
Driven
The TransformObject nodes to drive, for example, “
spine_01 spine_02 spine_03”. This parameter also accepts APEX path patterns, so you can specify tags in this field, for example, #spine.
It’s good practice to also specify the bind tag that is set up by default on the FK transform component’s Tags parameter. The FK transform component is normally the first component used to start building a rig. Including the bind tag helps to ensure that you don’t include other controls that might have inherited, for example, the spine tag. So for this component, you can set Driven to “#bind & #spine”.
Driver ¶
Make sure the control names are unique. To avoid naming conflicts when creating multiple spines, you can specify the spine segment using the string “{segment}”. For example, if your segment is named spine (Segments is set to spine), you can set Root Name to {segment}_root_ctrl. The value of Segments replaces the string “{segment}”, so the root control is named spine_root_ctrl.
COG Name
The name of the COG control. This is the main parent of the spine.
Root Name
The name of the root control.
Root CV Name
The name of the root tangent CV.
Mid Name
The name of the middle control.
Tip CV Name
The name of the tip tangent CV.
Tip Name
The name of the tip control.
End Name
The name of the end control. This control doesn’t affect the rest of the spine.
Root CV Offset
The offset to add to the root tangent CV.
Tip CV Offset
The offset to add to the tip tangent CV.
End Control Offset
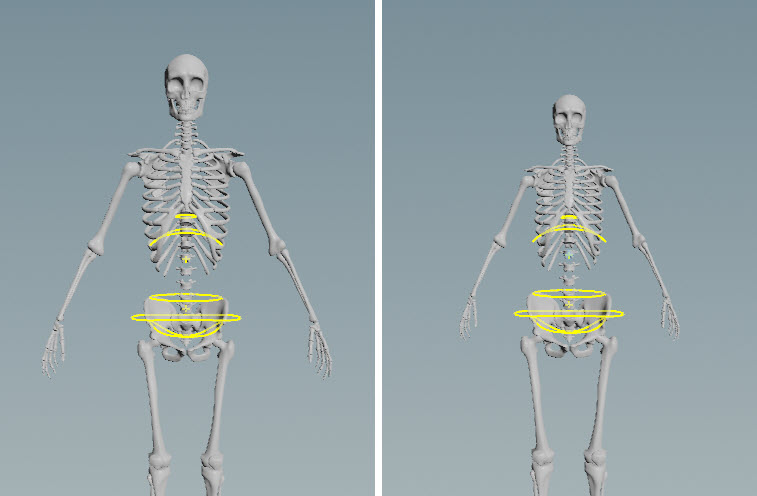
The offset to add to the end control. The end control is offset from the joint at the tip control. If you move the end control away from the tip joint, the control still pivots about that joint:
COG Position
The position of the COG control.
Level COG
When turned on, levels the angle of the COG control. When turned off, the COG control is rotated to match the angle of the joint it was created from.
Scale Inheritance
Sets the scale inheritance of the spine controls.
Promote T
When turned on, promotes the translate component of the spine controls.
Promote R
When turned on, promotes the rotate component of the spine controls.
Promote S
When turned on, promotes the scale component of the spine controls.
Parent ¶
Root
The parent of the root control. If left empty, the root control is parented to its associated TransformObject node’s parent. For example, if the root control sits at node
C_pelvis, and C_pelvis's parent is C_root, then the root control will be parented to C_root. If you are setting up multiple spines, you can leave this field empty.
You can also set parent tags on the skeleton, and use the parent tag plus the Segments tag to get the parent for each segment. For example, if your segment is named spine (Segments is set to spine), and you tag the parent joint with spine_parent, then you can set Root to {segment}_parent. The value of Segments is used to replace the string “{segment}”.
To unparent the root control, set this parameter to an underscore (“_”).
This parameter accepts APEX path patterns, so you can specify tags in this field, for example, #<tag>.
Tip
The parent of the tip control. If left empty, the tip is parented to the Root. To unparent the tip control, set this parameter to an underscore (“_”). This parameter accepts APEX path patterns, so you can specify tags in this field.
CV
The parent of the CVs. If left empty, the CVs are parented to the closest outer control. To unparent the CV controls, set this parameter to an underscore (“_”). This parameter accepts APEX path patterns, so you can specify tags in this field.
Tags ¶
Shape ¶
The APEX Configure Controls SOP provides more options for changing the look of the controls.
Shape
The shape of the mid and end controls. It can be set to any of the built-in APEX control shapes.
Color
The color of the control shapes. To inherit the shape color from the skeleton, set this value to (0, 0, 0).
Translate
The translation of the spline control shapes.
Rotate
The rotation of the control shapes.
Scale
The scale of the control shapes. To inherit the shape scale from the skeleton, set this value to (0, 0, 0).
| See also |