| On this page | |
| Since | 21.0 |
This node scatters stamps (or multiple stamps) along a curve in the image. The node provides layers and parameters that let you further configure the randomization. When no stamps input is wired in, the node stamps a star pattern.
Note
You must wire in a curve input to use this node.
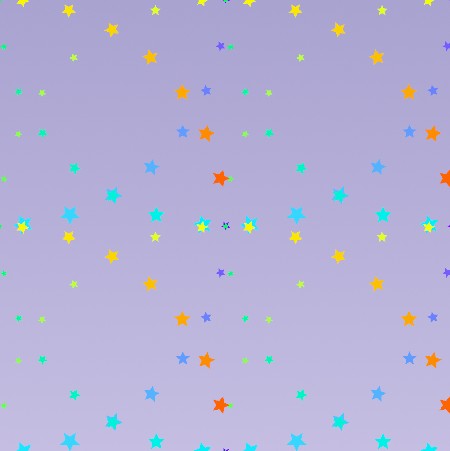

Turn on Mirror Stamps when you want to mirror stamps across the curve’s tangent.
For example, use this node to create patterns with stamps, such as orienting the stamps towards the center of a circle.
Parameters ¶
Signature
The layer type that the node outputs.
See Signatures for more information.
Scattering ¶
Distribution
The distribution mode for how to scatter the stamps along the curve.
Distance
Scatter stamps equidistant from each other based on a set distance.
Scatter
Scatter stamps randomly based on a density input or the Max Count.
By Count
Scatter stamps randomly based on a specific count.
Segment Length
When Distribution is Distance, this is the maximum segment length of resulting edges.
Maximum Segments
When Distribution is Distance, this is the maximum number of edges.
Density Layer Mask
When Distribution is Scatter, this is the amount of the density input’s mono value to mix in with the Density value. Higher values mix in more of the input’s value. Lower values mix in less of the input’s value.
Density Scale
When Distribution is Scatter, this is the amount to scale the density of the points.
This parameter doesn’t apply when Max Count is on.
Max Count
When Distribution is Scatter or By Count, this is the amount of points to generate.
Relaxation
When Distribution is Scatter or By Count, this relaxes points by pushing them away from each other to avoid clumping. More relaxation iterations result in further separation between the points.
Relaxation is done gradually to avoid chaotic behavior and allow control over how much relaxation takes place.
Scatter Seed
The seed value for all randomization that deals with stamp placement. This includes jitter, density, angle and direction, scale, and stretch.
Scale ¶
Scale Layer Mask
The amount of the scale input’s mono value to mix in with the Scale value, which impacts the stamps' scale. Higher values mix in more of the input’s value. Lower values mix in less of the input’s value.
Scale
The scale of the stamps in image space. Use the dropdown menu to set the method of post-processing that applies to the scale of the stamps.
Uniform
No post-processing.
Variance
Apply random variance to the scale.
Min/Max
The minimum and maximum range of values that each stamp randomly picks from, and then multiplies against the original Scale.
Scale Variance
The amount of random variance to apply to the scale. This is applied as a post-process.
If Scale is 1 and Scale Variance 1 for example, this represents a 100% range in sizes. This means the output stamps have a random scale from 0.5 * Scale to 2.0 * Scale.
Min Scale
The minimum value that the stamps can randomly select, and then multiply against the original Scale. This is applied as a post-process.
Max Scale
The maximum value that the stamps can randomly select, and then multiply against the original Scale. This is applied as a post-process.
Apply Scale along Curve
Applies a ramp along the curve and multiplies the ramp by the stamp’s scale. The curve of the ramp determines which stamps to scale.
See Ramp parameters for more information.
Curve ¶
Cut Curves by Relative Arc Length
Solves for the actual location halfway along the curve as measured by distance. This is useful since curves have a parameterization that doesn’t match the actual distance along the curve. For example, a curve of 0.5 isn’t halfway along the curve but halfway along its parameterization.
Start Point
The start point in image space of the curve.
End Point
The end point in image space of the curve.
Smoothing
The amount of smoothing to apply to the curve.
Mirror and Offset ¶
Mirror Stamps
Creates a mirrored version of the stamps on the other side of the curve. Use the dropdown menu to set the mirror’s behavior.
Treat Independently
Apply randomization and scattering separately.
Note
This mode’s angle mirroring isn’t done as a post-process, so any randomization breaks the mirroring of the angle across the curve.
Use Values from Original
Takes the mirrored curve and copies all values and looks from the original to the mirrored copy. This occurs after the randomization and scattering.
Use Values from Mirrored Copy
Takes the original curve and copies all values and looks from the mirrored to the original copy. This occurs after the randomization and scattering.
From Curve
The amount to perpendicularly offset the stamps from the tangent of the curve.
Mirrored From Curve
The amount to perpendicularly offset the mirrored stamps from the tangent of the curve.
Jitter
The amount of random position offset to add to each stamp’s position on the grid.
Offset along Curve
The amount to offset the stamp placement along the curve.
Angle ¶
Angle Layer Mask
The amount of the angle input’s mono value to mix in with the Angle value, which impacts the degree of the stamps' angles. Higher values mix in more of the input’s value. Lower values mix in less of the input’s value.
Note
For the stamp input, the incoming stamp’s upward direction is taken as its forward position and points along the curve in default behavior. The following example shows this behavior using an upward facing arrow as the stamp input.
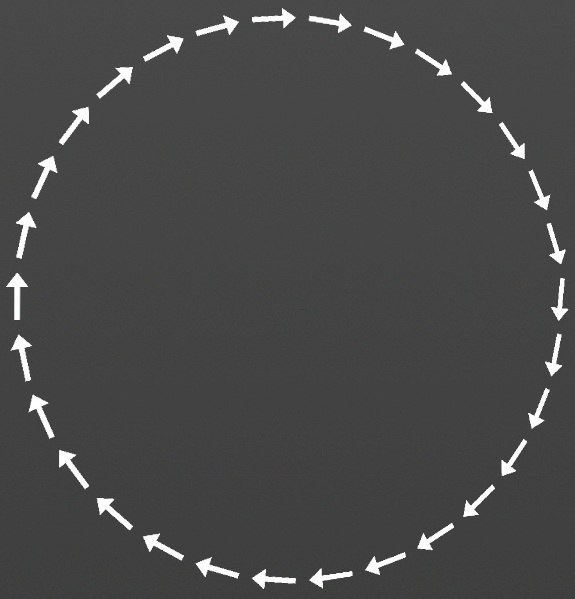
Direction Layer Mask
The amount of the direction input’s UV value to mix in with the Angle value, which impacts the direction of the stamps' angles. Higher values mix in more of the input’s value. Lower values mix in less of the input’s value.
Angles Relative to Curve Direction
Accounts for the curve’s usual direction when calculating the angle.
Angle
The angle in degrees to rotate each stamp. Use the dropdown menu to set the method of post-processing that applies to the angle of the stamps.
Uniform
No post-processing.
Variance
Apply random variance to the angles.
Min/Max
The minimum and maximum range of values in degrees that each stamp randomly picks from, and then multiplies against the original angle.
Angle Variance
The amount of random variance to apply to the angles. This is applied as a post-process.
For example, a value of 30 makes each stamp have a random offset between -30 degrees and 30 degrees.
Min Angle
The minimum degree that the stamps can randomly select, and then multiply against the original Angle. This is applied as a post-process.
Max Angle
The maximum degree that the stamps can randomly select, and then multiply against the original Angle. This is applied as a post-process.
Increment per Stamp
The amount of angle increase for each stamp along the curve.
For example, if Increment per Stamp is 10 and your curve has 36 points, each stamp progressively rotates more and the end stamp makes a full rotation.
Round to Multiples
Snaps all stamps to a specified angle. This is applied as a post-process.
Stretch ¶
Stretch Layer Mask
The amount of the stretch input’s UV value to mix in with the Stretch X and Stretch Y values, which impacts the XY scale. Higher values mix in more of the input’s value. Lower values mix in less of the input’s value.
Stretch Mode
The method of post-processing that applies to the non-uniform scale (stretch) of the stamps.
Uniform
No post-processing.
Variance
Apply random variance to the scale of the X and Y-axes.
Min/Max
The minimum and maximum range of values that each stamp randomly picks from, and then multiplies against the original Stretch X and Stretch Y.
Stretch X
The scale of the stamps along the X-axis in image space.
Stretch Y
The scale of the stamps along the Y-axis in image space.
Stretch Variance
The amount of random variance to apply to the scale of the X and Y-axes. This is applied as a post-process.
If Stretch X is 1, Stretch Y is 0, and Stretch Variance is 1, 0 for example, this represents a 100% range in sizes. This means the output stamps have a random scale from 0.5 * Stretch x to 2.0 * Stretch x.
Min Stretch
The minimum value that the stamps can randomly select, and then multiply against the original Stretch X and Stretch Y. This is applied as a post-process.
Max Stretch
The maximum value that the stamps can randomly select, and then multiply against the original Stretch X and Stretch Y. This is applied as a post-process.
Stretch along Curve
Applies two ramps along the curve to scale stamps along the X and Y-axes.
Stretch X along Curve
Applies a ramp along the curve and multiplies the ramp by the stamp’s scale along the X-axis. The curve of the ramp determines which stamps to scale.
See Ramp parameters for more information.
Stretch Y along Curve
Applies a ramp along the curve and multiplies the ramp by the stamp’s scale along the Y-axis. The curve of the ramp determines which stamps to scale.
See Ramp parameters for more information.
Color and Blending ¶
Blend ¶
Blend Method
When mulitple stamps overlap, this controls how they blend together.
Depth-Sorted Over
Presort the points by their depth. The node renders the farthest points first, so closer points paint over them. This option can be expensive since it requires sorting.
Unsorted Depth-Weighted Over
Apply a non-linear weighting that approximates depth-sorting without the need for sorting.
Add
Add the overlapping pixel values of the stamps together.
Subtract
Subtract the original pixel value from the new overlapping stamp’s pixel value. This method works better when you're not subtracting from zero.
Multiply
Multiply the overlapping pixel values of the stamps together. This method works better when the background starts at a non-zero value.
Maximum
Compare the stamps along with the background color and use the maximum value.
Minimum
Compare the stamps along with the background color and use the minimum value.
Use Sort Layer
Multiply the Depth-Sorted Over or Unsorted Depth-Weighted Over sort values by the sort input’s value.
Apply Sort along Curve
Applies a ramp along the curve to sort the stamps.
See Ramp parameters for more information.
Color ¶
Color Seed
The seed value for randomization that deals with stamp color and alpha.
Color Layer Mask
The amount of the color input’s RGB value to mix in with the Stamp Color value, which impacts the stamps' tint. Higher values mix in more of the input’s value. Lower values mix in less of the input’s value.
Stamp Color
A tint for the stamp. Use the dropdown menu to set how the color applies to the stamps.
Uniform
Apply the same color to each stamp.
Variance
Apply random variance to the hue, saturation, and value of the stamps.
Random from Ramp
Pick randomly from a color ramp.
See Ramp parameters for more information.
Ramp along Curve
Applies a ramp along the curve and multiplies the ramp by the stamp’s color. The curve of the ramp determines which colors apply to the stamps.
See Ramp parameters for more information.
Hue
The amount of random variance to apply to the hue. This is applied as a post-process.
If set to 30 for example, the stamps randomly pick a hue offset from the range of 0 to 30.
Saturation
The amount of random variance to apply to the saturation. This is applied as a post-process.
If set to 0.5 for example, the stamps randomly pick a saturation from the range of 0 to 0.5.
Value
The amount of random variance to apply to the value. This is applied as a post-process.
If set to 0.5 for example, the stamps randomly pick a value from the range of 0 to 0.5.
Alpha ¶
Alpha Layer Mask
The amount of the alpha input’s mono value to mix in with the Stamp Alpha value, which impacts the stamps' alpha. Higher values mix in more of the input’s value. Lower values mix in less of the input’s value.
Stamp Alpha
The amount of black (0) and white (1) by which to multiply the stamp’s alpha. Use the dropdown menu to set how the alpha applies to the stamps.
Uniform
Apply the same amount of alpha to each stamp.
Variance
Apply random variance to the alpha of the stamps.
Random from Ramp
Pick randomly from a mono ramp.
See Ramp parameters for more information.
Ramp along Curve
Applies a ramp along the curve and multiplies the ramp by the stamp’s alpha. The curve of the ramp determines how much alpha applies to the stamps.
See Ramp parameters for more information.
Alpha Variance
The amount of random variance to apply to the alpha. This is applied as a post-process.
Background ¶
Background Color
The initial background color of the space around the stamps.
Background Alpha
The initial background alpha of the space around the stamps.
Stamp Selection ¶
Selection Mode
The stamps to place in the image. When no stamps input is wired in, this parameter applies to the default star pattern.
Cycle
Loop through all stamps in a repetitive cycle.
Random
Randomly choose stamps based on the Select Seed.
Layer Select
Use the select input to choose stamps. The parameter uses the first stamp when a pixel value is 0.0 and the last stamp when a pixel value is 1.0.
Limit Selection
Limits the maximum number of stamps that the node uses.
Select Seed
The seed value for randomization that deals with stamp selection.
Options ¶
Filter
The method used to sample the image.
See Filters for more information.
Wrap Mode
The wrapping behavior of the stamps.
Auto
Wrap points outside of the main tile (whose size is controlled by Tile Size) back into the tile when the size_ref input image’s Border type is Wrap.
Off
Don’t wrap the stamps.
On
Wrap points outside of the main tile (whose size is controlled by Tile Size) back into the tile. This makes the main tile seamlessly repeat.
Tile Size
When Wrap Mode is Auto or On, this is the size (in image space) of the region to wrap into. The resultant image periodically repeats in this size.
Inputs ¶
size_ref
A representative layer that determines the size of the output image and controls the metadata.
curve
The curve along which to scatter stamps.
Note
You must wire in a curve input to use this node.
density
An optional layer that’s scaled by the Density Layer Mask parameter and performs rejection sampling on the created stamps.
direction
An optional layer that’s scaled by the Direction Layer Mask parameter and controls the direction of the created stamps' angles. For example, wire the Slope Direction COP into this input.
angle
An optional layer that’s scaled by the Angle Layer Mask parameter and rotates the stamps. A pixel value of 0 is 0 degrees and a pixel value of 1 is 360 degrees.
scale
An optional layer that’s scaled by the Scale Layer Mask parameter and multiplies the uniform scale of the stamps.
stretch
An optional layer that’s scaled by the Stretch Layer Mask parameter and multiplies the non-uniform scale of the stamps.
color
An optional layer that’s scaled by the Color Layer Mask parameter and multiplies the color of the stamps.
alpha
An optional layer that’s scaled by the Alpha Layer Mask parameter and multiplies the alpha of the stamps.
sort
An optional layer that controls depth-based sorting.
select
An optional layer that, when Selection Mode is set to Layer Select, chooses which stamps to use. This chooses from either the stamps input or the default star pattern when there’s no stamps input.
stamps
An optional layer that provides stamps. Wire in a cable to use up to 8 stamps.
Outputs ¶
result
The layer with the stamping applied.
id
The ID attribute of the stamp that contributed the most to this pixel or, if that attribute isn’t present, the point number.
uv
The UV coordinates of the stamp that contributed the most to this pixel. This is in image space.
| See also |