| On this page | |
| Since | 21.0 |
This node generates various noises defined by phasor kernels. A phasor kernel is a local filter that defines sine and cosine waves in a small neighborhood around a center point. By default, the noise resembles a wave pattern. When the Signature is any channel except Mono, the node generates additional phasor noises for each component of the set channel and each phasor noise applies the same parameters. For example, a UV channel results in one phasor noise for the U layer and one for the V layer.
Note
Patterns that this node generates are procedural rather than simulation-based, so the results may look more artificial than those from real-time simulations.
This noise provides you with more control over its direction and intervals. Though you can use OpenCL code with sine and cosine functions to generate similar patterns, this node has better performance.
For example, use this node to create the following effects:
-
wood grain
-
ripples on water surfaces
-
windblown textures in deserts
Tip
Wire in other noise types (for example, Fractal Noise or Worley Noise) to create more intricate and unique patterns.
Parameters ¶
Signature
The layer type that the source outputs.
See Signatures for more information.
Rotate Channel
When Signature is any channel except Mono, this is the amount to rotate the noise in the additional channels. Each layer is rotated by a different angle offset. When set to 0, the output image is equivalent to when the Signature is Mono.
For example, when Signature is RGBA, the node generates four separate phasor noises that each have a unique rotation.
Range ¶
Amplitude
The amount by which to multiply the noise, which the node applies before the Center adjustment.
For example, a value of 0.5 makes a pixel value of 0.5 become 0.25.
Note
Layers can store negative numbers and values above 1, so this may result in out-of-bounds values. You can use a Clamp COP to enforce the range afterwards.
Center
The center of the output noise range, which offsets the pixel values.
For example, a value of 0.5 makes a pixel value of 0.5 become 1.
Noise Contrast
The amount of contrast to apply to the noise before the Amplitude and Center parameters. You can use this parameter to make the noise more extreme without exceeding the 0 to 1 range.
Pattern ¶
Type
Sets the type of noise and, when set to Phasor Wave, the periodic function (wave type).
Phasor Wave
Consists of the Sine, Rectangle, and Saw profiles. These provide consistent wave patterns across the entire surface.
Phasor Noise
Defined by the Gabor Noise. It has a sharper shape than the Gabor Noise.
Gabor Noise
The result of summing the phasor kernel values. This means overlapping kernel regions either amplify or cancel each other out. These overlapping areas create softened gray, ripple patterns.
Intensity Field
The set of intensity values that define the Phasor Wave and Gabor Noise, which outputs soft ripple patterns with varying wave widths. This type can create more organic, natural-looking forms than the other noise types.
When set to Phasor Wave, you can choose one of the following periodic functions:
Sine
Sets the periodic function as the sine function . This creates smooth contrast transitions between the top and bottom peaks.
Rectangle
Sets the periodic function as a rectangular function . This creates distinct black-and-white regions, resulting in vivid, cartoon-like wave patterns.
Saw
Sets the periodic function as a sawtooth function . This creates a linear contrast transition from the top to bottom peak, sharply emphasizing both extremes.
Element Size
The size of the wave’s width in the noise. You can turn on the Per-Component Controls button to adjust this further using the Element Scale parameter.
Warning
This parameter can output undesired results if you use values outside the 0 to 1 range.
Element Scale
When the Per-Component Controls button is on, this is the per-axis scaling of the element size.
Offset
The amount to offset the entire noise function in image coordinates.
Tile Size
The size of a single tile of noise. The noise periodically repeats in this size. The size is in image coordinates, so the default is for the entire default canoncial image. If you have a non-square image, this should match the aspect ratio.
Note
If on, values for parameters like Element Size are rounded or clamped to make them valid. This is because these types of parameters must meet certain conditions for the noise to be tileable.
Wave Bias
When Type is Phasor Wave, this is the peak position of each periodic function.
When a bias input is wired in, that value is used instead of the Wave Bias.
Blending Radius
The radius of the phasor kernels. Higher values increase the radius of the phasor kernels so they overlap more, while lower values decrease their radius so there is more space between each kernel.
Seed
The seed that the random number generator uses. Change this parameter to generate a new position for the kernels.
Kernels
The number of disk-shaped local regions where the primary sine and cosine waves are defined.
Bias ¶
These parameters apply when you wire in a bias input and the Type is Phasor Wave.
Blur
The amount to blur the input image. Blurring results in a softened bias boundary.
Strength
The strength of bias blending. When set to 0, this displays the original noise and doesn’t apply bias blending.
Scale ¶
These parameters apply when you wire in a scale input. This input’s value is multiplied by the Element Size.
Blur
The amount to blur the input image. Blurring results in a softened scale boundary.
Strength
The strength of scale blending. When set to 0, this displays the original noise and doesn’t apply scale blending.
3D Noise ¶
3D Noise
Evaluates the noise in a 3D space. Use these parameters to control the third dimension, while the first two dimensions are the location in the image.
Animate
Implicitly adds time to the third coordinate.
Pulse Length
The interval length (in seconds) of the noise’s pulse in the third dimension. Lower values increase the rate at which the noise switches its appearance, while higher values decrease this rate.
Time Offset
The amount of time (in seconds) that’s added to the start frame.
Time Scale
The amount of time (in seconds) by which to multiply the start frame. Higher values increase the rate at which the noise switches its appearance, while lower values decrease this rate.
Loop Length (sec)
This is the time (in seconds) at which to repeat the noise. This clamps other options to enforce periodic behavior. Turn this on to generate animations that seamlessly loop.
When off, the animation generally doesn’t repeat after any amount of time.
Rotate ¶
Rotate Pattern
The amount to rotate the phasor kernels. When Uniform, this sets a uniform initial angle for each phasor kernel. When Set Varying, this lets you set Rotation Varying to randomize the initial angle of each phasor kernel.
Note
Each phasor kernel has a certain angle. As kernels are rotated, the noise pattern is rotated. Since kernel intersections change depending on the rotation, it behaves differently from a standard image rotation.
Rotation Varying
When Rotate Pattern is Set Varying, this is the randomized initial angle of phasor kernels. When set to 0, the value displays uniformed initial angles.
Use Secondary Rotation
Sets secondary phasor kernels at the same location of the initial phasor kernels.
Rotate Pattern
The amount to rotate the additional phasor kernels. When Uniform, this sets a uniform initial angle for each secondary phasor kernel. When Set Varying, this lets you set Rotation Varying to randomize the initial angle of each secondary phasor kernel.
Rotation Varying
When Rotate Pattern is Set Varying, this is the randomized initial angle of the secondary phasor kernels. When set to 0, the value displays uniformed initial angles.
Post Processing ¶
Note
The node applies the post-processing operations in the order they're listed.
Fold
Sets the noise values to the absolute value. For example, a pixel value of -2 becomes 2.
Note
This parameter doesn’t impact the output when there’s only positive values.
Complement
Sets the pixel value x to 1 - x.
Note
This method works for values in the 0 to 1 range. For images outside of this range, using Complement results in negative or out of range values.
Bias
The amount to pull the medium grey values (around 0.5) towards zero (if Bias is less than 1) or one (if Bias is greater than 1). A bias value of 0.5 doesn’t affect the values.
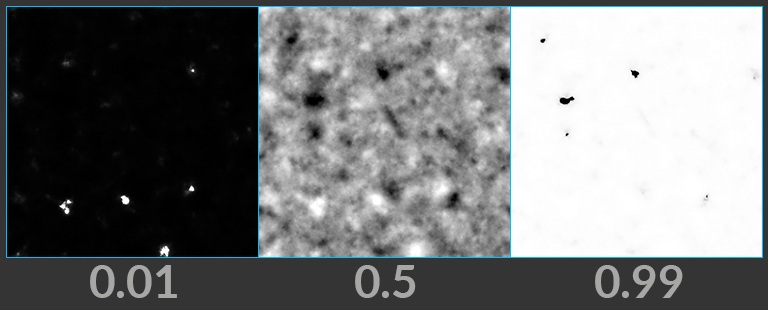
Gain
The amount to pull the medium grey values (around 0.5) together, while values around 0 and 1 are pulled apart. A gain value of 0.5 doesn’t affect the noise values.
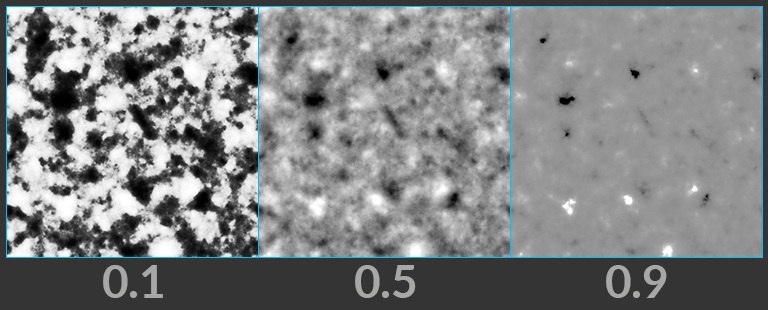
Gamma
The overall gamma of the generated noise. Values greater than 1 increase the range of values in originally bright areas, which darkens the noise. Values less than 1 stretch out the range of values for originally dark areas, which increases the overall brightness of the noise.
Contrast
The amount to expand or shrink the overall range of tonal values. Each noise value is pushed towards (if Contrast is less than 1) or away from (if Contrast is greater than 1) medium grey values (around 0.5).
Note
This is not the same as Noise Contrast, which appears in some noise nodes and applies contrast during the noise function.
Clamp Minimum
Clamps values below the specified threshold.
Clamp Maximum
Clamps values exceeding the specified threshold.
Inputs ¶
size_ref
A representative layer that determines the size of the output image and controls the metadata.
pos
An optional UV layer with a value that’s used instead of the pixel’s image coordinates for the noise.
time
An optional layer with a value that each pixel uses for the time.
bias
An optional layer with a value that’s used for the peak position of each periodic function of the Phasor Wave noise type. When wired in, this value is used instead of the Wave Bias. Use the Bias parameters to blur this value.
scale
An optional layer with a value that’s multiplied by the Element Size. Use the Scale parameters to blur this value.
direction
An optional UV layer to set the initial angle of phasor kernels.
Outputs ¶
noise
The computed noise.
| See also |