| On this page | |
| Since | 19.0 |
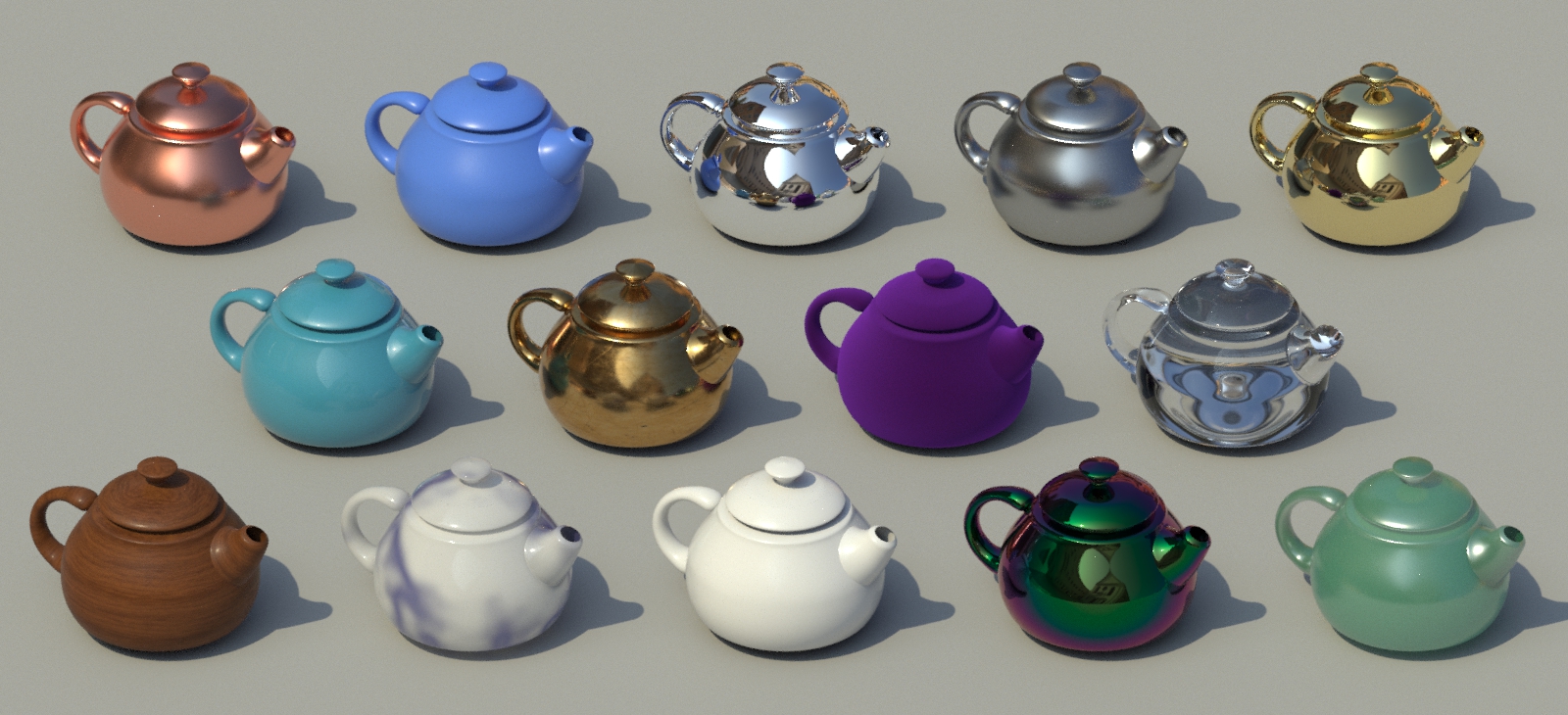

MaterialX Standard Surfaceは、物理ベースのシェーダで、様々なマテリアルを表現するのに便利です。
このMaterialXの実装は、Georgiev et al氏によるAutodesk Standard Surfaceに基づいています。
Tips ¶
-
法線マップを-1から1の範囲に変換したいのであれば、その法線マップを
MtlX Normalmapに接続してください。
-
ガラスをレンダリングする場合:
-
Render Geometry Settingsを使用して、目的のオブジェクトの Enable Caustics を有効にしてください。
-
-
発光マテリアルをKarmaでもっと効率的にレンダリングしたいのであれば、
Render Geometry Settingsを使用して、目的のオブジェクトの Treat As Light Source を有効にしてください。
パラメータ ¶
Base
拡散反射の強度の乗数。

Base Color
拡散反射の色。

Diffuse Roughness
拡散反射の粗さ。 値が高いほど、表面がより平坦で暗く見えるようになります。
Metalness
マテリアルの金属っぽさの度合いを指定します。 最大値に設定すると、完全スペキュラと複雑なフレネルが使用されて、表面が金属のような見た目になります。

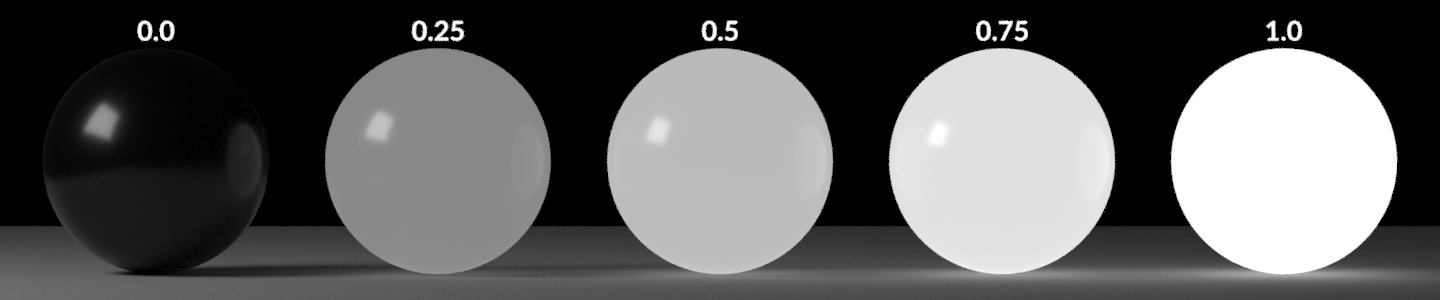
Specular
スペキュラの強度の乗数。

0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0
Specular Color
スペキュラの色味。
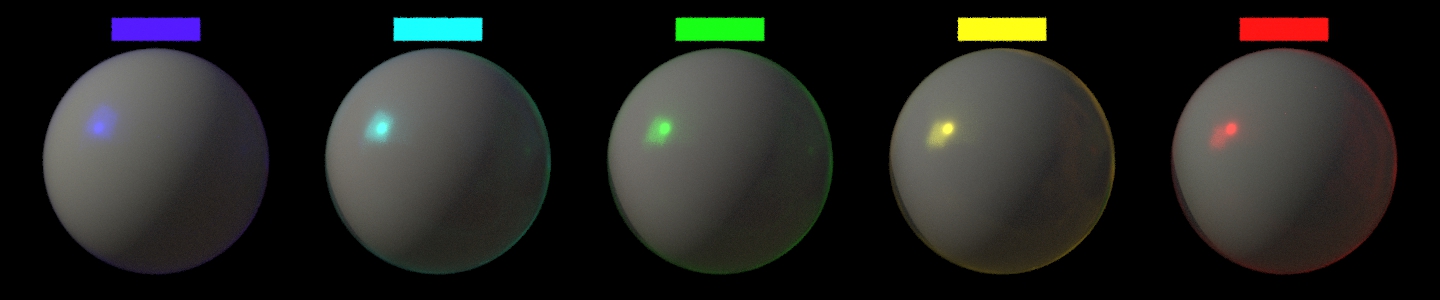
Specular Roughness
スペキュラの粗さ。 値が低いほど反射が鮮明になり、値が高いほど反射がぼやけます。

Index of Refraction
スペキュラの屈折率。 これは透過マテリアルの屈折も設定します。


Specular Anisotropy
反射光と透過光の方向の偏向によって、マテリアルの見た目が特定の方向で粗くなったり、つやが出たりします。
Specular Rotation
サーフェス法線を基準としたスペキュラ異方性の軸の回転。
Transmission
ガラスや水といったマテリアルの表面を通過する光の透過度。 値が大きいほど、マテリアルは透明になります。

Transmission Color
透過光の色味。
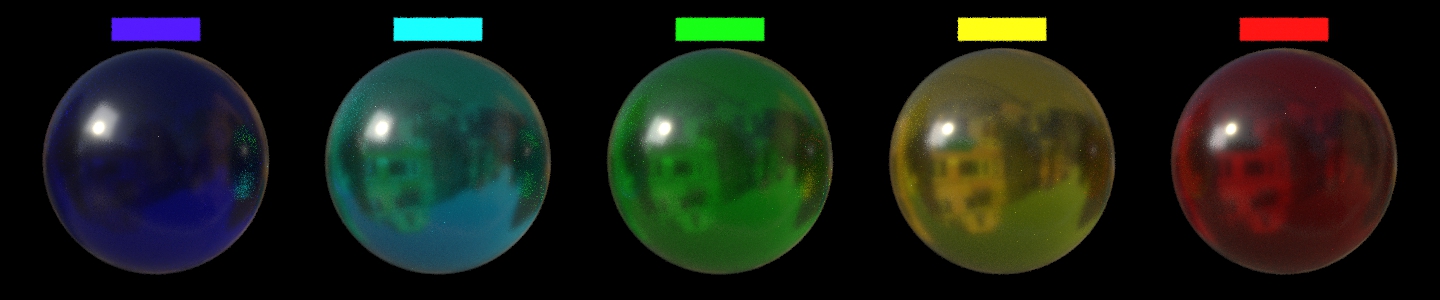
Transmission Depth
ランバート・ベールの法則に応じて光がマテリアル内を通過して完全に Transmission Color になるまでの深さを指定します。

Transmission Scatter
Karmaでサポートされていません。
内部媒体の散乱係数。 海、蜂蜜、氷、すりガラスなど嵩のある液体や非常に濃い液体に適しています。
Transmission Anisotropy
Karmaでサポートされていません。
散乱の偏向、異方性の度合い。
Transmission Dispersion
屈折率が波長間で可変する度合いを示した分散度。

Transmission Roughness
スペキュラ粗さの上に追加する粗さ。 プラスの値は反射よりも屈折をぼかし、マイナスの値は屈折のぼかしが弱くなります。
Subsurface
拡散反射とサブサーフェススキャタリングのブレンド。1.0の値は、完全サブサーフェススキャタリング、0.0の値は拡散反射のみを意味します。

Subsurface Color
サブサーフェススキャタリング効果の色。
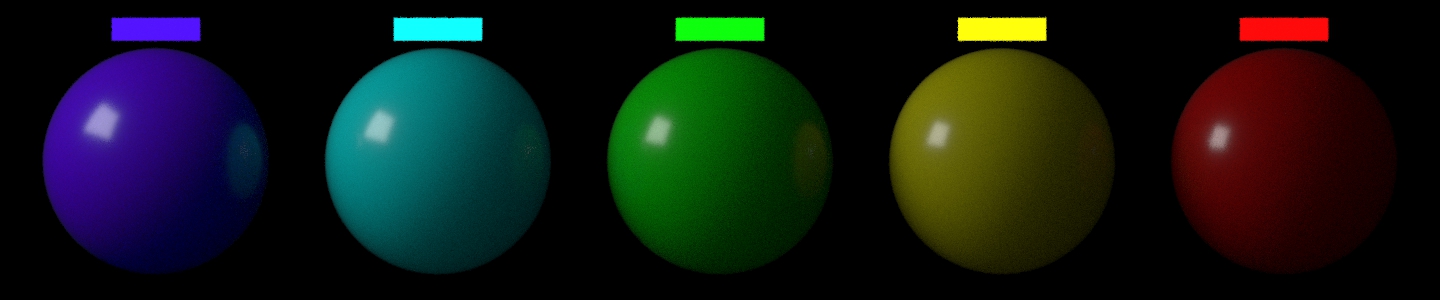
Subsurface Radius
平均自由経路。 光がサーフェス内部で散乱する前に移動可能な距離。 カラーコンポーネント毎に別々に半径を指定できるようにベクトル値を使用します。
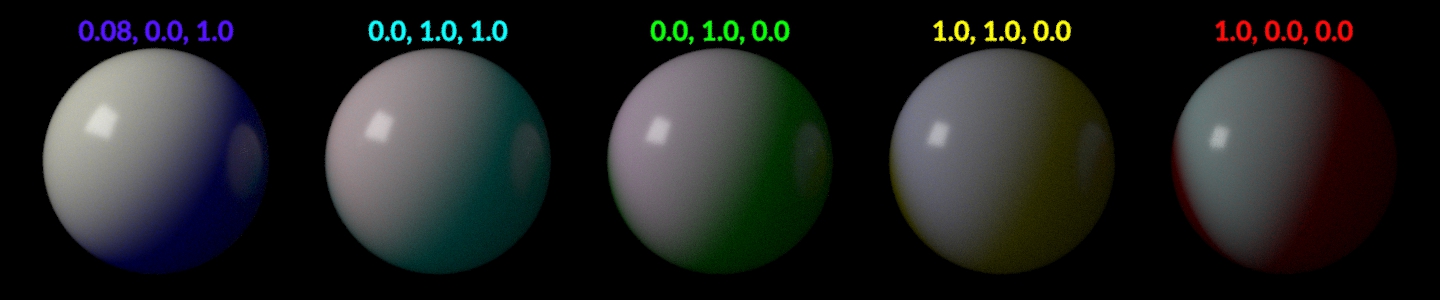
Subsurface Scale
Subsurface Radius の値に対するスカラーウェイト。
Subsurface Anisotropy
サブサーフェススキャタリングの方向。 0は光を等方に散乱させ、プラスの値は前方に、マイナスの値は後方に光を散乱させます。
Sheen
ベルベットやサテンといったマイクロファイバーや布を模倣するのに使えるSheen(光沢)レイヤのウェイト。

Sheen Color
Sheenレイヤの色。

Sheen Roughness
Sheenレイヤの粗さ。

Coat
マテリアル上に反射するクリアコートレイヤのウェイト。 車の塗装や油っぽい層などのマテリアルに使用します。

Coat Color
クリアコートレイヤの透明の色。

Coat Roughness
クリアコート反射の粗さ。値が低いほど、反射が鮮明になります。

Coat Anisotropy
クリアコートレイヤの方向バイアスまたは異方性の度合い。
Coat Rotation
クリアコートレイヤの異方性効果の回転。
Coat Index of Refraction
クリアコートレイヤの屈折率。
Coat Normal
クリアコートレイヤ用の入力法線。
Coat Affect Color
クリアコートレイヤ下の拡散反射とサブサーフェススキャタリングの彩度を制御します。
Coat Affect Roughness
クリアコートレイヤ下のスペキュラとサブサーフェススキャタリングの粗さを制御します。
Thin Film Thickness
サーフェス上の薄膜レイヤの厚み。 マルチトーンの車の塗装やシャボン玉などのマテリアルに使用します。

Thin Film Index of Refraction
マテリアルを覆う媒体の屈折率。

Emission
放出される白熱光の量。
Emission Color
発光の色。

Opacity
マテリアル全体の不透明度。

Thin Walled
有効にすると、サーフェスが両面化され、限りなく薄い厚みを表現するので、木の葉や紙などの薄いオブジェクトに適しています。 Thin Walled を有効にすると、 Transmission と Subsurface のパラメータの効果が制限されます。 薄い厚みの透過は屈折を無効にします。
Transmission Color と Transmission Roughness のパラメータのみが薄い厚みの透過に影響を与えます。

Subsurface Color パラメータのみが薄い厚みのサブサーフェススキャタリングに影響を与えます。

入力 ¶
Normal
入力のジオメトリ法線。-1から1までの範囲のワールド空間ベクトル(デフォルトは現在のワールド空間法線)。
Tangent
入力のジオメトリ接線。-1から1までの範囲のワールド空間ベクトル(デフォルトは現在のワールド空間接線)。
出力 ¶
出力値は、同じ名前のサーフェスコンテキスト内の出力変数に接続することができます。
out
surface
| See also |