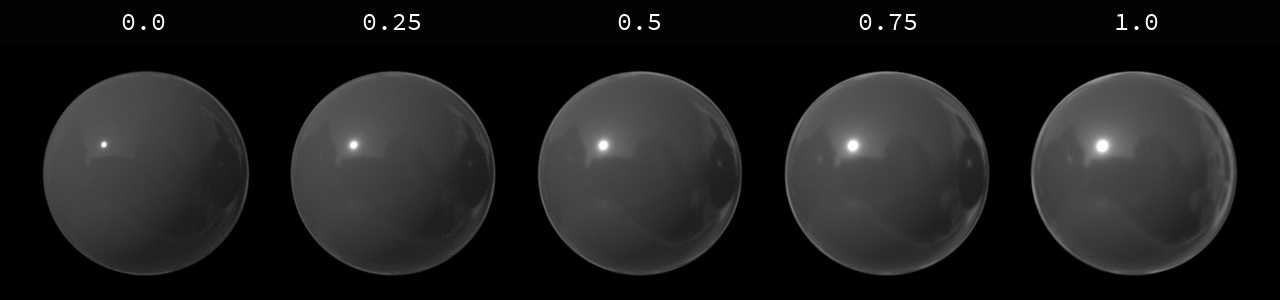
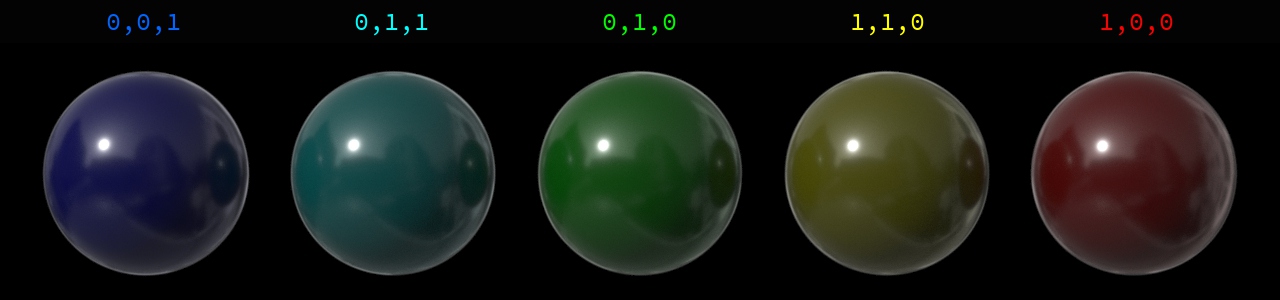
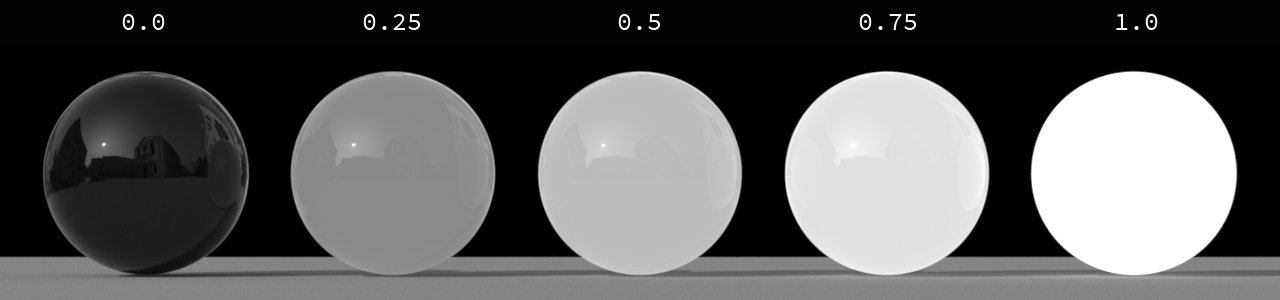
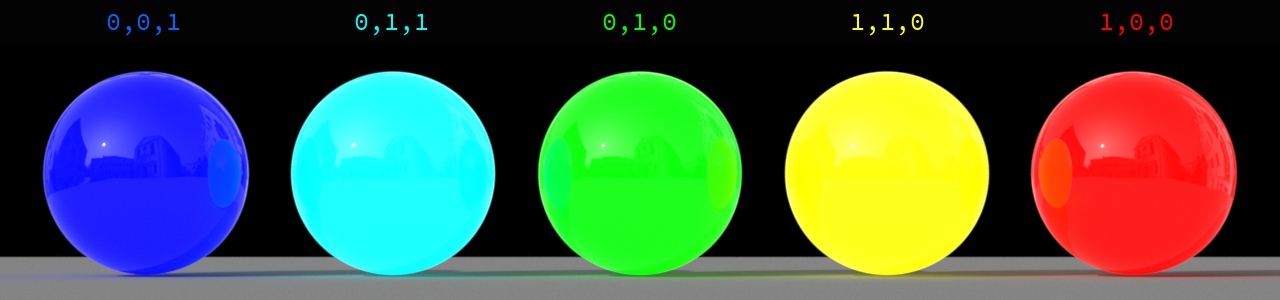
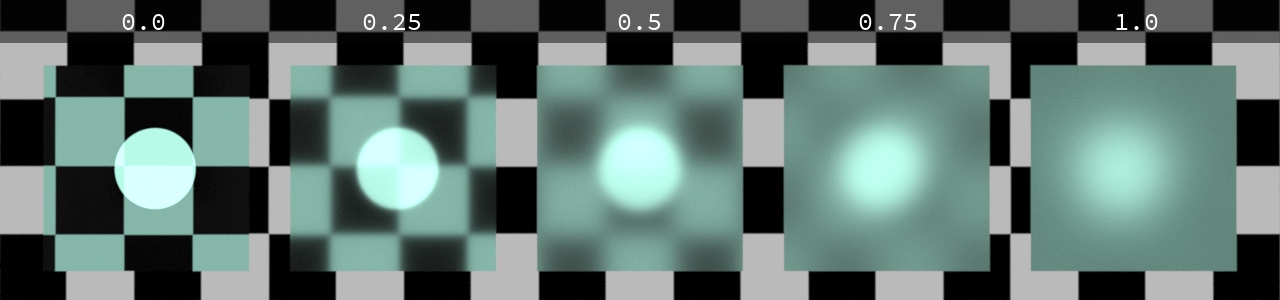
-
Absolute
Computes the absolute value of the argument.
-
Add
Outputs the sum of its inputs.
-
Add Attribute
Adds a new attribute.
-
Add Constant
Adds the specified constant value to the incoming integer, float,
vector or vector4 value.
-
Add Joint
Adds a KineFX joint to the geometry.
-
Add Point
Adds points to the geometry.
-
Add Point to Group
Adds the point specified to the group given.
-
Add Primitive
Adds primitives to the geometry.
-
Add Steer Force
Multiply steerforce by steerweight attributes and normalize results by total steerweight.
-
Add Vertex
Adds vertices to the geometry.
-
Add Wind Force
Layers a wind force onto a simulation.
-
Advect by Volumes
Advects a position by a set of volume primitives stored in a disk file.
-
Agent Clip Catalog
Returns all of the animation clips that have been loaded for an agent primitive.
-
Agent Clip Length
Returns the length (in seconds) of an agent’s animation clip.
-
Agent Clip Names
Returns an agent primitive’s current animation clips.
-
Agent Clip Sample
Samples an agent’s animation clip at a specific time.
-
Agent Clip Sample Rate
Returns the sample rate of an agent’s animation clip.
-
Agent Clip Times
Returns the current times for an agent primitive’s animation clips.
-
Agent Clip Weights
Returns the blend weights for an agent primitive’s animation clips.
-
Agent Convert Transforms
Converts transforms between local space and world space for an agent primitive.
-
Agent Layer Bindings
Returns the transform that each shape in an agent’s layer is bound to.
-
Agent Layer Name
Returns the names of the current layers or collision layers of an agent.
-
Agent Layer Shapes
Returns the names of the shapes referenced by an agent primitive’s layer.
-
Agent Layers
Returns all of the layers that have been loaded for an agent primitive.
-
Agent Rig Children
Returns the child transforms of a transform in an agent primitive’s rig.
-
Agent Rig Find
Finds the index of a transform in an agent primitive’s rig.
-
Agent Rig Parent
Returns the parent transform of a transform in an agent primitive’s rig.
-
Agent Transform Count
Returns the number of transforms in an agent primitive’s rig.
-
Agent Transform Names
Returns the name of each transform in an agent primitive’s rig.
-
Agent Transforms
Returns the current local or world space transforms of an agent primitive.
-
Align
Computes a matrix representing the rotation around the axes normal to two vectors by the angle which is between the two vectors.
-
Alpha Mix
Takes two values for alpha based on the surface orientation relative
to the camera and blends between the two with a
rolloff as the bias control, effectively removing the silhouettes of the
geometry edges.
-
Ambient
Generates a color using ambient lighting model calculation.
-
And
Performs a logical and operation between its inputs and returns 1 or 0.
-
Anti-Aliased Flow Noise
Generates anti-aliased (fractional brownian motion) noise by using
the derivative information of the incoming position to compute
band-limited noise.
-
Anti-Aliased Noise
Generates anti-aliased noise by using the derivative information of the incoming position to compute band-limited noise.
-
Anti-Aliased Ramp Parameter
-
Append
Adds an item to an array or string.
-
Arctangent
Performs the atan2() function
-
Array Contains
Checks whether a value exists in an array.
-
Array Find Index
Finds the first location of an item in an array or string.
-
Array Find Indices
Finds all locations of an item in an array or string.
-
Array Length
Produces the length of an array.
-
Attenuated Falloff
Computes attenuated falloff.
-
Average
Outputs the average of its inputs.
-
Average Vector Component
Computes the average value of a vector argument.
-
BSDF Tint
Tints a BSDF with separate control over colorization and luminance.
-
Bake Exports
Export shading for use in bake image planes
-
Bias
-
Bind
Represents an attribute bound to VEX.
-
Bind Point Transform
Binds a KineFX point transform with a point index.
-
Blend Regions
Takes a float input as a bias to blend between three input
regions.
-
Blend Transforms
Blends between two KineFX transformation matrices.
-
Block Begin
Marks the start of a code block.
-
Block Begin For
Marks the start of a for loop block.
-
Block Begin For-Each
Marks the start of a for-each loop block.
-
Block Begin If
Marks the start of an if code block.
-
Block End
Marks the end of a code block.
-
Block End Break-If
Marks the end of a code block.
-
Block End While
Marks the end of a while code block.
-
Bounding Box
Returns two vectors representing the minimum and maximum corners of the bounding box for the specified geometry.
-
Box Clip
Clips the line segment defined by p1 and p2 to the bounding box
specified by the min and max corner points.
-
Boxes
Generates repeating filtered squares.
-
Bricker
Generates a brick pattern based on the parametric s and t
coordinates.
-
Brushed Circles
Outputs an angle that gives the appearance of a circular brush pattern when used with anisotropy direction.
-
Brushed Metal Shader
A basic brushed metal shader.
-
Bump Noise
Displaces surfaces along their normal using anti-aliased noise, and
returns the displaced surface position, normal, and displacement amount.
-
Bump To Normal Map
Compute a tangent-space normal map from a bump map
-
Burlap
Generates a burlap displacement pattern useful for simulating rough
cloth or weave patterns.
-
Burlap Pattern
Returns float between 0 and 1 which defines a burlap pattern useful for simulating rough cloth or weave patterns.
-
COP Input
Returns a pixel value in one of the 4 input COPs connected to the VEX
COP.
-
CVEX Shader Builder
A node that implements a CVEX shader using its children VOPs.
-
Car Paint Shader
Simulates car paint with embedded metallic flakes and a coat layer.
-
Cavities
Produces a surface displacement that simulates small surface damage
using anti-aliased noise of various frequencies.
-
Ceiling
Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to the
argument.
-
Cellular Cracks
Generates a cellular crack displacement suitable for simulating skin,
leather, dried earth, and all kinds of crusts.
-
Cellular Noise
Computes 2D, anti-aliased cellular noise suitable for shading.
-
Character to String
Converts an unicode codepoint to a UTF8 string.
-
Checkered
Returns number between 0 and 1 which defines a checkered pattern useful for visualizing parametric or texture coordinates.
-
Clamp
Clamps the input data between the minimum and maximum values.
-
Class Cast
Downcasts a generic (anonymous) co-shader object to a specific co-shader
-
Classic Shader
Flexible material including multiple reflection layers, subsurface scattering, refractions and displacement.
-
Classic Shader Core
A powerful, highly flexible, generic surface shader with displacement.
-
Cloud Noise
Generates 1D noise used for cloud noise generation.
-
Collect
-
Collide Geometry
Collides the specified joint with the target geometry.
-
Color Correction
Provides a means to change the hue, saturation, intensity, bias, gain and gamma of the input color.
-
Color Map
Looks up a single sample of RGB or RGBA color from a disk image.
-
Color Mix
Computes a blend (or a mix) of its two color inputs, and outputs the
resulting color.
-
Color Transform
-
Combine Local Transform
Combines local and parent KineFX transforms with scale inheritance.
-
Compare
Compares two values and returns true or false.
-
Complement
Computes the complement of the argument by subtracting the argument
from 1.
-
Composite
-
Compute Lighting
Computes lighting using Physically Based Rendering.
-
Compute Normal
This node gives finer control over handling of the normal attribute in VOPs.
-
Compute Tangents
Compute surface tangents in different ways.
-
Conductor Fresnel
Outputs a physically correct reflection factor for conductive materials.
-
Conserve Energy
Clamp the reflectivity of a bsdf to 1.
-
Constant
Outputs a constant value of any VEX data type.
-
Contour
Increases or decreases contrast for values at the bottom of the input range.
-
Copy
Takes a single input of any data type.
-
Cosine
Performs a cosine function.
-
Crackle
Returns float between 0 and 1 which defines a crackle pattern useful for simulating the fine grain texture in skin or on a much larger scale dried mudflats.
-
Create Point Group
Creates a new point group with the name specified.
-
Cross Product
Computes the cross product between two vectors, defined as the vector
perpendicular to both input vectors.
-
Curl Noise
Creates divergence-free 3D noise using a curl function.
-
Curl Noise 2D
Creates divergence-free 2D noise using a curl function.
-
Curvature
Computes surface curvature.
-
Curve Solver
Positions and orients KineFX points from a curve and a list of segment lengths.
-
Decal
An OTL that performs composting of texture maps.
-
Degrees to Radians
Converts degrees to radians.
-
Delayed Load Procedural
-
Delayed Read Archive
-
Depth Map
Works on an image which was rendered as a z-depth image, returning
the distance from the camera to the pixel (or plane) in
question.
-
Determinant
Computes the determinant of a 4×4 or 3×3 matrix.
-
Dictionary Keys
Produces the keys of a dictionary.
-
Dictionary Length
Produces the length of a dictionary.
-
Direct Lighting
Internal VOP used to compute direct lighting.
-
Direction to Child
Computes the direction to a KineFX joint’s child.
-
Direction to Parent
Computes the direction to a KineFX joint’s parent
-
Dirt Mask
Masks crevices or exposed edges
-
Displace
Displaces surface position and modifies surface normals.
-
Displace Along Normal
Displaces the surface along the surface normal by a given amount.
-
Displacement Texture
Modifies normals and/or positions based on a texture map.
-
Distance
Returns the distance between two 3D or 4D points.
-
Distance Point to Line
Returns the closest distance between a point and a line segment
defined by two end points.
-
Divide
Outputs the result of dividing each input value by the next.
-
Divide Constant
Divides the incoming integer, float, vector or vector4 value by the
specified constant value.
-
Dot Product
Computes the dot product between two vectors.
-
Dual Rest
Outputs sanitized dual rest values based.
-
Dual Rest Solver
Sanitizes dual rest attribute data for easier use.
-
Edge Falloff
Creates a smooth roll-off of the input color from the center of the
geometry to the edges, based on the surface normal.
-
Eggshell Pattern
Returns a new surface normal (N) which has a slight fine grained bump on it.
-
Eigenvalues
-
Ends With
Result 1 if the string ends with the specified string.
-
Environment Map
Sets the environment map (on an infinite sphere) and returns its
color.
-
Euler to Quaternion
Builds a quaternion with the given euler rotation.
-
Exponential
Computes the exponential function of the argument.
-
Extract Local Transform
Computes a local transform for a KineFX point using its and its parent’s world transforms.
-
Extract Transform
Extracts the translation, rotation, scale or shear component of a 4×4
transform matrix.
-
Fake Caustics
Outputs and opacity value which can be used to approximate caustic lighting effects.
-
Fast Shadow
Sends a ray from the position P along the direction specified by the
direction D.
-
Fibratus
Generates a 2D, fiber like cloud pattern.
-
Field Name
Provides a fallback value for a field/attribute if the field does not
exist or the given field name is an empty string.
-
Field Parameter
Provides a fallback value for a field/attribute if the field does not
exist or the given field name is an empty string.
-
Filament Sample
-
Filter Point Transforms
Find a point in an array and return the transforms in the corresponding arrays.
-
Filter Pulse Train
Filters the input.
-
Filter Shadow
Sends a ray from the position P along the direction specified by the
direction D, a…
-
Filter Step
Computes the anti-aliased weight of the step function.
-
Filter Width
This function returns the square root of the area of a 3D input or the length of the derivative of a float input, such as s or t.
-
Find Attribute Value
-
Find Attribute Value Count
-
Find Attribute Value by Index
-
Find Point Transform
Find a point on a given geometry and return its transforms.
-
Fit Range
Takes the value in the source range and shifts it to
the corresponding value in the destination range.
-
Fit Range (Unclamped)
Takes the value in the source range and shifts it to
the corresponding value in the destination range.
-
Float to Integer
Converts a float value to an integer value.
-
Float to Matrix
Converts sixteen floating-point values to a 4×4 matrix value.
-
Float to Matrix2
Converts four floating-point values to a matrix2 value.
-
Float to Matrix3
Converts nine floating-point values to a matrix3 value.
-
Float to Vector
Converts three floating-point values to a vector value.
-
Float to Vector2
Converts two floating-point values to a vector2 value.
-
Float to Vector4
Converts four floating-point values to a vector4 value.
-
Floccus
Generates a 2D, locks of wool like cloud pattern.
-
Floor
Returns the largest integer less than or equal to the argument.
-
Flow Noise
Generates 1D and 3D Perlin Flow Noise from 3D and 4D data.
-
For Each Transform
Perform the same operation on an array of transforms.
-
Fraction
Computes the fractional component of the argument.
-
Fractus
Generates a 2D, ragged, broken up like cloud pattern.
-
Fresnel
Computes the Fresnel reflection/refraction contributions
given a normalized incident ray, a normalized surface normal, and an
index of refraction.
-
From NDC
Transforms a position from normal device coordinates to the
coordinates in the appropriate space.
-
From NDC
Transforms a position from normal device coordinates to the
coordinates in the appropriate space.
-
From Polar
Converts polar coordinates to cartesian coordinates.
-
Front Face
Returns the front facing normal of a surface, given a surface normal
(N) and an incident ray (I).
-
Fur Guide Global Variables
Provides outputs representing commonly used input variables of fur guide
shader network.
-
Fur Guide Output Variables and Parameters
Provides inputs representing the output variables of a fur guide shader
network.
-
Fur Procedural
Creates a set of hair-like curves across a surface at render time.
-
Fur Skin Global Variables
Provides outputs representing commonly used input variables of fur skin
shader network.
-
Fur Skin Output Variables and Parameters
Provides inputs representing the output variables of a fur skin shader
network.
-
Furrows
Displaces the surface along the surface normal by an amount equal to
the value of an anti-aliased cosine wave.
-
Fuzzy And
Performs a fuzzy and operation between its inputs and returns a value between 0 and 1.
-
Fuzzy Defuzz
Performs a defuzzify operation between its input fuzzy sets and returns a crisp value.
-
Fuzzy Inference
Performs a fuzzy inference operation over each input to determine the truth of the fuzzy set defined on this node.
-
Fuzzy Inference Mirror
-
Fuzzy Input
Performs a fuzzify operation that calculates a fuzzy value given a membership function and an input crisp value.
-
Fuzzy Not
This operator performs a fuzzy not operation on an integer or float value.
-
Fuzzy Obstacle Sense
Detects obstacles in an agent’s field of view.
-
Fuzzy Or
Performs a fuzzy or operation between its inputs and returns a value between 0 and 1.
-
Gain
-
Gather Loop
Sends rays into the scene and contains a subnetwork of VOPs to operate on the information gathered from the shaders of surfaces hit by the rays.
-
Gaussian Random
Generates a random number fitting a Gaussian distribution.
-
Gaussian Random UV
Generates a random number fitting a Gaussian distribution.
-
General Fresnel
Computes the Fresnel reflection/refraction contributions and vectors for objects with or without depth.
-
Generic Shader
Represents a shader.
-
Geometry VOP Global Parameters
Provides outputs that represent all the global variables for the
Attribute VOP network types.
-
Geometry VOP Output Variables
Simple output variable for Geometry VOP Networks.
-
Get Attribute
-
Get BSDF Albedo
Compute the reflectivity of a bsdf.
-
Get Blur P
-
Get CHOP Attribute
Returns a CHOP attribute value in one of the 4 input CHOPs connected to the Channel VOP.
-
Get Channel Transform
Returns a transform value built from 9 channels from one of the 4 input CHOPs connected to the Channel VOP.
-
Get Channel Value
Returns a sample value in one of the 4 input CHOPs connected to the Channel VOP.
-
Get Channel Value by Name
Returns a sample value in one of the 4 input CHOPs connected to the Channel VOP.
-
Get Descendant Transforms
Traverse the hierarchy from a given point and return their transforms.
-
Get Dictionary Element
Gets a specified value from dictionary.
-
Get Element
Gets a specified element from array.
-
Get FBIK Attributes
Retrieve configuration values for the Physical Full-Body IK solver from point attributes.
-
Get Full Body COM
Return the computed center-of-mass for the given KineFX geometry.
-
Get Joint Chain Axes
Computes a set of orthogonal axes centered at a KineFX joint.
-
Get Layer Export
Obtains a value of the export variable added to the Shader Layer struct.
-
Get Matrix Component
Extracts a 4×4 matrix component.
-
Get Matrix2 Component
Extracts a 2×2 matrix3 component.
-
Get Matrix3 Component
Extracts a 3×3 matrix3 component.
-
Get Object Transform
Gets the transform matrix of a named object in camera (current) space.
-
Get PTexture ID
-
Get Parent
Finds the parent of a joint within a KineFX skeleton.
-
Get Parent Transform
Gets the transformation of a joint’s parent within a KineFX skeleton.
-
Get Point Transform
Returns a point transform for a given point index.
-
Get Point Transforms
Returns arrays of point transforms given an array of point IDs.
-
Get Primitive ID
-
Get Vector Component
Extracts a vector component.
-
Get Vector2 Component
Extracts a vector2 component.
-
Get Vector4 Component
Extracts a vector4 component.
-
Get a CHOP Channel Value
Evaluates a CHOP channel and return its value.
-
Get a Channel or Parameter Value
Evaluates a channel (or parameter) and return its value.
-
Get an Object Transform
Evaluates an OBJ node’s transform
-
Gingham Checks
Generates anti-aliased gingham checks similar to a tablecloth
pattern.
-
Global Variables
Provides outputs that represent all the global variables for the
current VOP network type.
-
Gradient 3D
Returns the gradient of a single channel 3D texture image at a
specified position within that image.
-
HSV to RGB
Converts HSV color space to RGB color space.
-
Hair Normal
Generates a normal vector which always faces the camera, parallel to the incidence vector.
-
Hair Shader
A powerful, highly flexible, general model for hair/fur shading.
-
Has Input
Returns 1 if the specified input (0-3) is connected.
-
Has Key
Returns if a dictionary has a key.
-
High-Low Noise
Computes a mix of high and low frequency, anti-aliased noise with a
wide range of applications.
-
Houdini Engine Procedural: Curve Generate
Cooks a SOP asset for each point in the source geometry and instances the generated curves onto the point.
-
Houdini Engine Procedural: Point Generate
Cooks a SOP asset for each point in the source geometry and instances the generated points onto the point.
-
Hue Shift
Uses the shift value to move the hue of the input color along the color wheel by the amount influenced by the amplitude.
-
IK Solver
Positions and orients points from a root position, end effector position target, and twist position using KineFX Inverse Kinematics.
-
If Connected
Passes through the value of the first input if the first input is
ultimately connected.
-
Illuminance Loop
Only available in Surface VOP networks.
-
Image 3D Iso-Texture Procedural
This procedural will generate an iso-surface from a 3D texture image (.i3d file).
-
Image 3D Volume Procedural
This procedural will generate a volume from a 3D texture image (.i3d file).
-
Import Attribute
Imports attribute data from the OP connected to the given input.
-
Import Detail Attribute
-
Import Displacement Variable
Imports the value of the specified variable from a displacement
shader and stores it in var.
-
Import Light Variable
Imports the value of the specified variable from a light shader and
stores it in var.
-
Import Point Attribute
-
Import Primitive Attribute
-
Import Properties from OpenColorIO
Imports a color space property from Open Color IO.
-
Import Ray Variable
Imports the value of the specified variable sent from a trace() function and
stores it in var.
-
Import Surface Variable
Imports the value of the specified variable from a surface shader and
stores it in var.
-
Import Vertex Attribute
-
Importance Remap
-
In Group
Returns 1 if the point or primitive is in the group specified by the string.
-
Indirect Lighting
Internal VOP used to compute indirect lighting.
-
Inline Code
Write VEX code that is put directly into your shader or operator
definition.
-
Insert
Inserts an item, array, or string into an array or string.
-
Instance with Hscript Procedural
Runs hscript for each point in the source geometry and instances the generated geometry to the point.
-
Integer to Float
Converts an integer value to a float value.
-
Integer to Vector
-
Intersect
Computes the intersection of a ray with geometry.
-
Intersect All
Computes all the intersections of a ray with geometry.
-
Invert
If given a 3×3 or 4×4 matrix, this operator computes its inverse (or just returns the input matrix if it detects singularity).
-
Irradiance
Computes the irradiance (the global illumination) at the point P with
the normal N.
-
Is Alphabetic
Result 1 if all the characters in the string are alphabetic.
-
Is Connected
Outputs 1 if the input is ultimately connected, otherwise it outputs
0.
-
Is Digit
Result 1 if all the characters in the string are numeric.
-
Is Finite
Returns 1 if the number is a normal number, ie, not infinite or NAN.
-
Is Fog Ray
Returns 1 if the shader is being evaluated from within a fog
shader.
-
Is Front Face
Returns true if the normal of the surface is forward facing, and
false if it isn’t.
-
Is NAN
Returns 1 if the number is not a number.
-
Is Shadow Ray
Returns 1 if the shader is being evaluated for shadow rays.
-
Jittered Hair Normal
-
Join Strings
Concatenate all the strings of an array inserting a common spacer.
-
Joint Angle
Gets the angle at the given joint in a KineFX skeleton.
-
Karma 2D Derivatives
Generates partial derivatives of input0 variable over input1
-
Karma AOV 2.0
Creates a shading signal for output to an AOV, as well as the render vars.
-
Karma Camera Falloff
Generate a smooth roll-off between surface normal and the camera ray.
-
Karma Fur
A physically-based hair and fur material with medulla support
-
Karma Hair
A physically-based hair and fur material.
-
Karma Hexagonal Tiling Texture
Seamless texturing and normal mapping without visible repetitions based on provided UV coordinates.
-
Karma Hexagonal Tiling Triplanar
Seamless texturing and normal mapping without visible repetitions involving triplanar projections and based on P.
-
Karma Light Filter Attenuation
Karma Light Filter that controls how the light intensity/color changes over distance.
-
Karma Light Filter Barndoor
Karma Light Filter that adds barndoors to a cone light.
-
Karma Light Filter Gel
Karma Light Filter that adjusts the color, intensity, or diffuse/specular of a light source.
-
Karma Light Filter Gobo
Karma Light Filter that projects the light source through a texture.
-
Karma Light Projection
You can use this utility node in a light filter network to get the UV coordinates of the current ray in the light’s projection space.
-
Karma Material Properties
Apply Karma geometry properties via shaders.
-
Karma Melanin
A physically-based hair and fur color definition.
-
Karma OCIO Color Transform
Transforms color spaces using Open Color IO.
-
Karma Physical Lens
A pre-made lens shader implementation with controls for most common lens shader effects, such as bokeh, chromatic aberrations, and tilt/shift.
-
Karma Physical Lens Core
The stripped down version of the physical lens.
-
Karma Point Cloud Read
This node opens a point cloud file and searches for points around a source position then returns a value of geometry attribute imported from pointcloud
-
Karma Pyro Fire Color
Creates a color value used to control the emission component of volume shading used for fire.
-
Karma Pyro Fire Emission
Creates emission to control the emission component of volume shading used for fire.
-
Karma Pyro Scatter Color
Creates a color value used to control the emission component of volume shading used for explosions.
-
Karma Pyro Scatter Emission
Creates emission to control the emission component of volume shading used for explosions.
-
Karma Pyro Shader
Flexible, production-quality smoke, cloud, fire, and explosion shader.
-
Karma Pyro Smoke Color
Creates a color value used to control the scattering and absorption component of volume shading.
-
Karma Pyro Volume Mask
Creates a volume mask used for volume shading.
-
Karma Ramp Constant
Look up the color/float at a certain index in a ramp.
-
Karma Ray Hit Level Falloff
Attenuate values based on bounces.
-
Karma Ray Import
Imports the value of the specified variable from Karma.
-
Karma Ray Switch
Evaluate a color or an input based on ray-type.
-
Karma Room Lens
Generates an interior room map
-
Karma Room Map
Creates a parallax projection of a room interior onto a flat plane
-
Karma Tangent Rotate
Rotates world-space tangents for anisotropic shaders like brushed metal.
-
Karma UV Lens
This is the Karma UV rendering lens shader.
-
Karma Volume
Karma XPU compatible node for building MaterialX volume shader
-
Karma Voronoi Noise 2D
Generates Voronoi noise
-
Karma Voronoi Noise 3D
Generates Voronoi noise
-
Karma Whitewater
Karma XPU compatible node for building MaterialX-based basic whitewater shader
-
Lambert
Generates a color using the Lambert diffuse lighting model calculation.
-
Layer Composite
Combines two layers using standard compositing operations.
-
Layer Mix
Outputs a mix of the two input layers, blended using the alpha value.
-
Layer Pack
Creates a Layer from individual shading components.
-
Layer Unpack
Unpacks the individual shading components from a layer.
-
Length
Computes the length of an array
-
Length
Computes the length of a 3D or 4D vector.
-
Lens Bokeh
A VOP that can generate different kinds of bokeh.
-
Lens Chromatic Aberration
A VOP that can generates the tint and index of refraction for chromatic aberration effects.
-
Lens Coordinates
A VOP that creates the jittered coordinates for Karma lens shaders.
-
Lens Distort
A VOP that generates the offsets required to distort a Karma lens shader.
-
Lens OpenCV Distort
A VOP that generates the NDC coordinates with the OpenCV lens distortion model applied on a Karma lens shader.
-
Lens Parameters
A VOP that generates the Karma lens shader inputs.
-
Lens Rolling Shutter
A VOP that generates a time offset to simulate rolling shutter in digital lenses.
-
Lens Shutter Curve
A VOP that manipulates the time distribution of lens shutters.
-
Lighting Model
Performs a lighting model calculation to generate a color.
-
Limits
Selectively clamps values to a minimum and/or maximum value.
-
Logarithm
Computes the natural logarithm function of the argument.
-
Look At
Computes a 3×3 rotation matrix to orient the z-axis along the vector
(to - from) under the transformation.
-
Look At (KinefX)
Applies a KineFX Look At constraint to a transform.
-
Look At Constraint
Applies a KineFX Look At constraint to a transform.
-
Luminance
Computes the luminance of the RGB color specified by the input parameter.
-
Make Instance Transform
Builds a general 4×4 transform matrix derived from the
standard copy/instance attributes
-
Make Space Transform
Returns the transformation matrix to transform from a transform space such as an object’s transform space to another space, such as world space.
-
Make Transform
Builds a general 4×4 transform matrix.
-
Mandelbrot Set
Generates a Mandelbrot pattern.
-
Map Point
Creates a dictionary that maps one KineFX point to another.
-
MatCap Shader
A Material Capture shader.
-
Material shader builder
A higher-level shader that can contain one or more sub-shaders, such as surface shaders, displacement shaders, and rendering properties.
-
Matrix to Float
Unpacks a 4×4 matrix into its sixteen components.
-
Matrix to Vector4
Unpacks a 4×4 matrix into its rows.
-
Matrix2 to Float
Unpacks a 2×2 matrix2 into its four components.
-
Matrix2 to Matrix3
Converts a 2×2 matrix to a 3×3 matrix.
-
Matrix2 to Matrix4
Converts a 2×2 matrix to a 4×4 matrix.
-
Matrix2 to Vector2
Unpacks a 2×2 matrix into its rows.
-
Matrix3 to Float
Unpacks a 3×3 matrix3 into its nine components.
-
Matrix3 to Matrix2
Converts a 3×3 matrix to a 2×2 matrix.
-
Matrix3 to Matrix4
-
Matrix3 to Quaternion
Converts a matrix3, representing a rotation, to a quaternion
representing the same rotation.
-
Matrix3 to Vector
Unpacks a 3×3 matrix into its rows.
-
Matrix4 to Matrix2
Converts a 4×4 matrix to a 2×2 matrix.
-
Matrix4 to Matrix3
-
Matte
Implements a matte shader that occludes geometry behind the surface
being rendered.
-
Max Vector Component
Computes the maximum value of a vector argument.
-
Maximum
Outputs the maximum value from its inputs.
-
Meta-Loop Import
Takes a handle generated by the Meta-Loop Start operator and will
import attributes…
-
Meta-Loop Next
Takes a handle generated by the Meta-Loop Start operator and will
iterate to the …
-
Meta-Loop Start
Opens a geometry file and
initializes the handle to iterate through all metaballs at the position
specified.
-
Metaball Attribute
Returns the value of the given point attribute at the specified
position in the metaball field.
-
Metaball Density
Returns the density of the metaball field at the specified
position.
-
Metaball Space
Transforms the specified position into the local space of the
metaball.
-
Metaball Weight
Returns the metaweight of the geometry at a given position.
-
Metadata
Returns true if the specified metadata exists.
-
Metadata
Returns metadata from one of the 4 input COPs connected to the VEX COP.
-
Method
Represents a method inside a class-based shader.
-
Method Call
Invokes a given method on a given struct or co-shader object.
-
Method Input
Represents a method argument list inside a class-based shader.
-
Method Subnet
Represents a method inside a class-based shader.
-
Min Vector Component
Computes the minimum value of a vector argument.
-
Minimum
Outputs the minimum value from its inputs.
-
Minimum Position
Given a position in world space, returns the position of the closest point on a given geometry.
-
Mix
Computes a blend (or a mix) of its input values using linear
interpolation.
-
Modulo
Computes the modulo of two values.
-
MtlX Absorption Vdf
Constructs a VDF for pure light absorption.
-
MtlX Absval
-
MtlX Acescg To Lin Rec709
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Acos
-
MtlX Add
-
MtlX Adobergb To Lin Rec709
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX And
-
MtlX Anisotropic Vdf
Constructs a VDF scattering light for a participating medium.
-
MtlX Artistic Ior
-
MtlX Asin
-
MtlX Atan2
-
MtlX Bias
-
MtlX Bitangent
-
MtlX Blackbody
Returns the radiant emittance of a blackbody radiator with the given temperature.
-
MtlX Blur
-
MtlX Bump
-
MtlX Burley Diffuse Bsdf
A BSDF node for Burley diffuse reflections.
-
MtlX Burn
-
MtlX Ceil
-
MtlX Cellnoise2D
2D cellular noise
-
MtlX Cellnoise3D
-
MtlX Checkers 2D
Checkerboard pattern.
-
MtlX Chiang Hair Absorption from Color
Calculates hair absorption from a color.
-
MtlX Chiang Hair BSDF
A BSDF node for Chiang hair shading model.
-
MtlX Chiang Hair Roughness
Calculates hair roughness for R, TT and TRT component.
-
MtlX Circle
A circle shape.
-
MtlX Circles 2D
Pattern of circles or rings.
-
MtlX Clamp
-
MtlX Cloverleaf
A cloverleaf shape.
-
MtlX Color Correct
-
MtlX Color Cubic Ramp
-
MtlX Color Ramp
-
MtlX Combine2
-
MtlX Combine3
-
MtlX Combine4
-
MtlX Conductor Bsdf
A reflection BSDF node based on a microfacet model and a Fresnel curve for conductors/metals.
-
MtlX Conical Edf
-
MtlX Constant
-
MtlX Contrast
Increase or decrease contrast of incoming float/color values using a linear slope multiplier.
-
MtlX Convert
-
MtlX Cos
-
MtlX Create Matrix
-
MtlX Create Matrix (3×3)
-
MtlX Crosshatch
A cross-hatch pattern.
-
MtlX Crossproduct
-
MtlX Deon Hair Absorption from Melanin
Calculates hair absorption from melanin parameters.
-
MtlX Determinant
-
MtlX Dielectric Bsdf
A reflection/transmission BSDF node based on a microfacet model and a Fresnel curve for dielectrics.
-
MtlX Difference
-
MtlX Directional Light
-
MtlX Disjointover
-
MtlX Disney Principled
-
MtlX Displacement
A constructor node for the displacement shader.
-
MtlX Distance
Measure distance between two points.
-
MtlX Divide
-
MtlX Dodge
-
MtlX Dot
-
MtlX Dotproduct
-
MtlX Exp
-
MtlX Extract
-
MtlX Facing Ratio
Generate a smooth roll-off between two vectors.
-
MtlX Facing Ratio
-
MtlX Float Cubic Ramp
-
MtlX Float Ramp
-
MtlX Floor
-
MtlX Fract
The fraction of a float or vector.
-
MtlX Fractal3D
Zero-centered 3D Fractal noise.
-
MtlX Frame
-
MtlX G18 Rec709 To Lin Rec709
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX G22 Ap1 To Lin Rec709
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX G22 Rec709 To Lin Rec709
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Gain
-
MtlX Generalized Schlick Bsdf
A reflection/transmission BSDF node based on a microfacet model and a generalized Schlick Fresnel curve.
-
MtlX Generalized Schlick Edf
A fresnel EDF.
-
MtlX Geometry Color
-
MtlX Geometry Property Value
-
MtlX Geometry Property Value Uniform
Reads uniform, non-varying asset path and string primvars.
-
MtlX Glossiness Anisotropy
-
MtlX Gltf Colorimage
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Gltf Image
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Gltf Iridescence Thickness
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Gltf Normalmap
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Gooch Shade
-
MtlX Grid
A grid pattern.
-
MtlX HSV to RGB
-
MtlX Hcatmullrom
-
MtlX Heighttonormal
-
MtlX Hexagon
A hexagon shape.
-
MtlX Hinvlinear
-
MtlX Hsvadjust
Adjust the hue, saturation and value of a color.
-
MtlX Huniformcubic
-
MtlX Huniformramp
-
MtlX If Equal
-
MtlX If Equal (Boolean)
-
MtlX If Greater
-
MtlX If Greater (Boolean)
-
MtlX If Greater or Equal
-
MtlX If Greater or Equal (Boolean)
-
MtlX Image
Samples data from a single image, or from a layer within a multi-layer image.
-
MtlX In
-
MtlX Inside
-
MtlX Invert
-
MtlX Invertmatrix
-
MtlX Layer
-
MtlX Light
-
MtlX Lin Adobergb To Lin Rec709
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Lin Displayp3 To Lin Rec709
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Line
A line shape.
-
MtlX Ln
-
MtlX Luminance
Output a grayscale luminance of a color.
-
MtlX Magnitude
-
MtlX Mask
-
MtlX Matte
-
MtlX Max
-
MtlX Measured Edf
Constructs an EDF emitting light according to a measured IES light profile.
-
MtlX Min
-
MtlX Minus
-
MtlX Mix
-
MtlX Modulo
-
MtlX Multiply
-
MtlX Noise2D
-
MtlX Noise3D
3D Perlin noise.
-
MtlX Normal
-
MtlX Normalize
-
MtlX Normalmap
-
MtlX Not
-
MtlX Open PBR Anisotropy
-
MtlX OpenPBR Surface
A physically-based uber-shader.
-
MtlX Oren Nayar Diffuse Bsdf
A BSDF node for diffuse reflections.
-
MtlX Out
-
MtlX Outside
-
MtlX Over
-
MtlX Overlay
-
MtlX PBR Texture Set
Texture sets for MtlX Standard Surface.
-
MtlX Place2D
Transform incoming UV texture coordinates for 2D texture placement.
-
MtlX Plus
-
MtlX Point Light
-
MtlX Position
-
MtlX Power
-
MtlX Premult
-
MtlX RGB to HSV
-
MtlX Ramp
A ramp that supports up to 10 control points.
-
MtlX Ramp Gradiant
A helper node that handles a single control point within a ramp
-
MtlX Ramp4
-
MtlX Ramplr
-
MtlX Ramptb
-
MtlX Random Color
Random RGB color pattern.
-
MtlX Random Float
Random float pattern.
-
MtlX Range
-
MtlX Rec709 Display To Lin Rec709
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Reflect
-
MtlX Refract
-
MtlX Remap
-
MtlX Rotate2D
Rotate a vector2 value about the origin in 2D.
-
MtlX Rotate3D
-
MtlX Roughness Anisotropy
-
MtlX Roughness Dual
-
MtlX Round
-
MtlX Safe Power
-
MtlX Saturate
Adjust the saturation of a color.
-
MtlX Screen
-
MtlX Separate Color 3
-
MtlX Separate Color 4
-
MtlX Separate Vector 3
-
MtlX Separate Vector 4
-
MtlX Separate2
-
MtlX Sheen Bsdf
A microfacet BSDF for the back-scattering properties of cloth-like materials.
-
MtlX Sign
-
MtlX Sin
-
MtlX Smoothstep
-
MtlX Splitlr
-
MtlX Splittb
-
MtlX Spot Light
-
MtlX Sqrt
-
MtlX Srgb Displayp3 To Lin Rec709
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Srgb Texture To Lin Rec709
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Standard Surface
A physically-based shader.
-
MtlX Standard Surface To Gltf Pbr
A new MaterialX Node
-
MtlX Standard Surface to USD Preview Surface
Translation shader from Standard Surface to USD Preview Surface.
-
MtlX Subsurface BSDF
A BSDF for true subsurface scattering.
-
MtlX Subtract
-
MtlX Surface
-
MtlX Surface Material
Constructs a surface shader describing light scattering and emission for closed 'thick' objects.
-
MtlX Surface Unlit
An unlit surface shader node.
-
MtlX Switch
-
MtlX Tan
-
MtlX Tangent
-
MtlX Texcoord
-
MtlX Tiled Circles
A tiled-circle pattern.
-
MtlX Tiled Cloverleafs
A tiled-cloverleaf pattern.
-
MtlX Tiled Hexagons
A tiled-hexagon pattern.
-
MtlX Tiled Image
Samples data from a single image, with provisions for tiling and offsetting the image across uv space.
-
MtlX Time
-
MtlX Transformmatrix
-
MtlX Transformnormal
-
MtlX Transformpoint
-
MtlX Transformvector
-
MtlX Translucent Bsdf
A BSDF node for pure diffuse transmission.
-
MtlX Transpose
-
MtlX Triangle Wave
A triangle-wave pattern.
-
MtlX Triplanar Projection
-
MtlX UDIM Offset
Manually set UDIM texture coordinates.
-
MtlX UDIM Patch
Extract the UDIM patch from texture coordinates.
-
MtlX USD Preview Surface
MaterialX flavor of USD Preview Surface shader
-
MtlX USD Primvar Reader
MaterialX flavor of USD Primvar Reader
-
MtlX USD Transform 2D
MaterialX flavor of USD Transform 2D shader
-
MtlX USD UV Texture
MaterialX flavor of USD UV Texture shader
-
MtlX USD UV Texture
MaterialX flavor of USD UV Texture 2.3 shader
-
MtlX Unified Noise 2D
-
MtlX Unified Noise 3D
-
MtlX Uniform Edf
An EDF node for uniform emission.
-
MtlX Unpremult
-
MtlX View Direction
-
MtlX Volume
A constructor node for the volume shader type.
-
MtlX Volume Material
A volume material.
-
MtlX Worley Noise 2D
-
MtlX Worley Noise 3D
-
MtlX Xor
-
MtlX Xxor
-
MtlX glTF Pbr
A PBR shader from glTF-2.0.
-
MtlX gltf image (vector)
A new MaterialX Node
-
Mtlx Complement
Returns complementary float value.
-
Mtlx Complement Color
Returns complementary RGB color
-
Multiply
Outputs the product of its inputs.
-
Multiply Add Constant
Will take the input value, add the pre-add amount, multiply by the
constant multiplier, then add the post-add amount.
-
Multiply Constant
Multiplies the incoming value by a constant.
-
Near Point
Finds closest point in a given geometry file.
-
Negate
Negates the incoming integer, float, vector or vector4 value.
-
Neighbor Count File
Count the number of connected points from a given point in a given geometry file (or op:path)
-
Neighbor File
Finds the nth neighbouring point for a given point in a given geometry file.
-
Neighbors
Retrieves an array of indices to the points connected to the given point.
-
Non-Deterministic Random
A non-deterministic random number generator.
-
Normal Clamp
Clamp shading normals to prevent bad reflection directions
-
Normal Falloff
Generates a falloff value based on the relationship between the normal and incident vectors.
-
Normalize
Normalizes a vector.
-
Not
This operator performs a logical not operation on an integer value,
returning 1 if the input is zero, and 0 if the input is non-zero.
-
Null
Passes the inputs to the output with an optional name change.
-
OCIO Color Transform
Transforms color spaces using OpenColorIO.
-
OCIO Color Transform View
Transforms color spaces into a View using OpenColorIO.
-
OSL Bias
-
OSL Calculate Normal
-
OSL Dx/Dy/Dz
-
OSL Environment Map
-
OSL Gain
-
OSL Generic Shader Builder
Implements an OSL shader.
-
OSL Logarithm
-
OSL Step
-
OSL Texture Map
-
OSL Transform
-
OSL Transform Color
-
Occlusion
Computes ambient occlusion at the point P with the normal N.
-
Ocean Sample Layers
Sample ocean values from layered ocean spectra at the specified position and time.
-
Offset Transform
Offsets a KineFX transformation matrix by the given transform.
-
OpenSubdiv Face Count
Returns the number of coarse faces in the subdivision hull
-
OpenSubdiv First Patch
Returns the patch of the first patch for a given face in the subdivision hull.
-
OpenSubdiv Limit
Evaluates a point attribute on the limit of a subdivision surface and all
partial derivatives with respect to the given attribute.
-
OpenSubdiv Limit Surface
Evaluates a point attribute on the limit of a subdivision surface.
-
OpenSubdiv Lookup Face
Outputs the Houdini face and UV coordinates corresponding to the given coordinates on an OSD patch.
-
OpenSubdiv Lookup Patch
Outputs the OSD patch and UV coordinates corresponding to the given coordinates on a Houdini polygon face.
-
OpenSubdiv Patch Count
Returns the number of patches in the subdivision hull
-
Or
This operator performs a logical or operation between its inputs and returns 1 or 0 .
-
Oren-Nayar
Generates a color using the Oren-Nayar diffuse lighting model calculation.
-
Orient
Reorients a vector representing a direction by multiplying it by a
4×4 transform matrix.
-
Oscillations
Returns an anti-aliased cosine or sine wave.
-
Outer Product
Computes the outer product of a pair of vectors.
-
Output Variables and Parameters
Provides inputs representing the writable output variables of
the shader network.
-
PBR Emission
Makes a shaded surface emissive.
-
PBR Hair Primary Reflection
Produce a hair BSDF.
-
PBR Hair Secondary Reflection
Produce a hair BSDF.
-
PBR Hair Transmission
Produce a hair BSDF.
-
PBR Lighting
Evaluate Lighting Using PBR.
-
PBR Metallic Reflection
Computes metallic reflections.
-
PBR Non-Metallic
Computes reflections and refractions for dielectric (non-metallic) materials.
-
PBR SSS
Creates an approximate SSS BSDF.
-
PBR Single Scatter
Creates a Single Subsurface Scatter BSDF.
-
PBR Volume Phase Function
-
Parameter
Represents a user-controllable parameter.
-
Parent Blend
Blends between KineFX transforms with an offset computed from the given bind transforms.
-
Parent Constraint
Constrains a KineFX point’s parent to a new world transform.
-
Periodic Noise
Generates 1D and 3D Perlin noise from 1D, 3D and 4D data.
-
Periodic Worley Noise
Computes 1D, 3D, and 4D tileable Worley noise, which is synonymous
with cell noise.
-
Photon Output Variables
Performs photon russian roulette.
-
Physical SSS
Outputs surface color based on a physically-based subsurface
scattering model. This node an do physically correct single scattering and/or multiple scattering.
-
Physically Based Diffuse
Produce a normalized diffuse bsdf.
-
Pixel Area
Returns the area of the current pixel after being transformed to the
new UV coordinate uvpos.
-
Pixel Derivative
Returns U and V derivatives of the current pixel.
-
Plane Clip
Clips the line segment defined by p1 and p2 against the 3D plane
defined by the following equation: plane.
-
Plane Count
Returns the number of planes in the input.
-
Plane Exists
Returns the name of the plane with the index plane_index in input input_index.
-
Plane Index
Returns the index of the plane with the name plane_index in input input_index.
-
Plane Name
Returns the name of the plane with the index plane_index in input input_index.
-
Plane Size
Returns the number of components in the plane with the index
plane_index in input input_index.
-
Point Bounding Box
Returns two vectors representing the minimum and maximum corners of the bounding box for the specified geometry.
-
Point Cloud Close
This node closes a point cloud handle opened by pcopen.
-
Point Cloud Export
This node exports point data while inside a pcunshaded loop.
-
Point Cloud Farthest
This node finds the farthest query point produced by pcopen.
-
Point Cloud Filter
This node filters the points queried by pcopen.
-
Point Cloud Find
Returns a list of closest points from a file
-
Point Cloud Find Radius
Returns a list of closest points from a file taking into account their radii.
-
Point Cloud Import
This node imports point data while inside a pciterate or pcunshaded loop.
-
Point Cloud Import by Index
This node imports point data from a pcopen.
-
Point Cloud Iterate
This node advances to the next iteration point returned by pcopen.
-
Point Cloud Num Found
This node returns the number of points found by pcopen.
-
Point Cloud Open
This node opens a point cloud file and searches for points around a source position.
-
Point Cloud Unshaded
This node advances to the next unshaded iteration point returned by pcopen.
-
Point Cloud Write
This function writes data for the current shading point out to a point cloud file.
-
Point Count
Returns the number of points for all primitives in the given
geometry.
-
Point In Group
Returns 1 if the point specified by the point number is in the group
specified by the string.
-
Point Instance Procedural
The underlying procedural when using Fast Point Instancing with the
instance render parameters.
-
Point Loop
Only available in Image3D VOP networks.
-
Point Replicate
The Point Replicate Procedural takes a number of input points and multiplies
them, and processes the result using a CVEX script.
-
Pop
Removes the last element of an array and returns it.
-
Pose Difference
Compute the difference between point transforms on two SOP skeletons.
-
Power
Raises the first argument to the power of the second argument.
-
Primitive Attribute
Evaluates an attribute for a given primitive at the specified uv parametric location.
-
Primitive Intrinsic
Evaluates an intrinsic on a given primitive.
-
Primitive Normal
Returns the normal of a primitive (defined by its number) at the
given uv parametric location.
-
Principled Shader
An artist-friendly shader that can model a large number of materials realistically.
-
Principled Shader
An artist-friendly shader that can model a large number of materials realistically.
-
Print
Generate a formatted text string.
-
Promote Layer Exports
Promotes the export variables from the Shader Layer struct to the parent
shader
-
Properties
-
Pyro Blackbody
Converts a temperature value into color (chroma) and intensity according
to the blackbody radiation model.
-
Pyro Color Correct
Provides color correction functions.
-
Pyro Color Model
Provides constant, artistic, and physically correct (blackbody) tint as
well as color correction functions.
-
Pyro Color Volume
Provides functions for editing color fields by conditioning the field
values, adding noise, filtering, and color correction.
-
Pyro Density Volume
Provides functions for editing fields such as density by conditioning
the field values, adding noise, and filtering.
-
Pyro Displace
-
Pyro Field
-
Pyro Noise
-
Pyro Shader
Flexible, production-quality smoke, fire, and explosions shader.
-
Pyro Shader - Classic
Flexible, production-quality fire and smoke shader.
-
Pyro Shader Core
Provides the core functionality needed to build a high-quality volumetric shader.
-
Quaternion
Takes an angle and an axis and constructs the quaternion representing the rotation about that axis.
-
Quaternion Conjugate
Computes the conjugate of a quaternion.
-
Quaternion Distance
Computes distance between quaternions in radians.
-
Quaternion Invert
Takes an quaternion inverts it..
-
Quaternion Multiply
Performs a quaternion multiplication with its two inputs.
-
Quaternion to Angle/Axis
Converts a quaternion to angle/axis form.
-
Quaternion to Euler
Converts a quaternion to a vector representing euler angles.
-
Quaternion to Matrix3
Converts a vector4, representing a quaternion, to a matrix3 value,
representing the same rotation.
-
RGB to HSV
Converts RGB color space to HSV color space.
-
RSL Gather Loop
Sends rays into the scene and contains a subnetwork of VOPs to operate on the information gathered from the shaders of surfaces hit by the rays.
-
Radians to Degrees
Converts radians to degrees.
-
Rainbow
Generates a non-repeating rainbow color ramp by modulating the hue
over the range of the parametric coordinate s and using the
given saturation and value to compute the HSV color.
-
Ramp Filter
Adds anti-aliased analytical filtering to the output of a Ramp Parameter
VOP.
-
Ramp Parameter
Represents a user-editable ramp parameter.
-
Ramps
Generates repeating filtered ramps.
-
Random
Generates a random number based on the position in one, three, or
four dimensions.
-
Random Binary Random Jitter
Generates a random number in a BRJ sequence.
-
Random Sobol
Generates a random number in a Sobol sequence.
-
Random Value
-
Ray Bounce Level
Returns the current ray-bounce level.
-
Ray Bounce Weight
Returns the amount that the current bounce level will contribute to
the final pixel color.
-
Ray Hit
This operator sends a ray from the position P along the direction
specified by the direction D, and returns the distance to the object
intersected or a negative number if not object found.
-
Ray Trace
Sends a ray starting at origin P and in the direction specified by
the normalized vector D.
-
Realistic Shoulder
Propagates rotation from the arm to the clavicle point in a KineFX skeleton.
-
Reflect
Returns the vector representing the reflection of the direction
against the normal vector.
-
Reflected Light
Computes the amount of reflected light which hits the surface.
-
Refract
Computes the refraction ray given an incoming direction, the
normalized normal and an index of refraction.
-
Refracted Light
Sends a ray starting at origin P and in the direction specified by
the normalized vector I.
-
Regex Find
Finds the given regular expression in the string.
-
Regex Findall
Finds all instances of the given regular expression in the string.
-
Regex Match
Result 1 if the entire input string matches the expression.
-
Regex Replace
Replaces instances of find_regex with replace_regex.
-
Regex Split
Splits the given string based on regex match.
-
Relative to Bounding Box
Returns the relative position of the point given with respect to the bounding box of the specified geometry.
-
Relative to Point Bounding Box
Returns the relative position of the point given with respect to the bounding box of the specified geometry.
-
Remove Index
Removes an item at the given index from an array.
-
Remove Key
Removes an item at the given key from a dictionary.
-
Remove Point
Removes points from the geometry.
-
Remove Primitive
-
Remove Value
Removes an item from an array.
-
Render State
Gets state information from the renderer.
-
RenderMan Bias
-
RenderMan Calculate Normal
-
RenderMan Deriv
-
RenderMan Du/Dv
-
RenderMan Environment Map
-
RenderMan Gain
-
RenderMan Illuminance Loop
-
RenderMan Illuminate Construct
-
RenderMan Import Value
-
RenderMan Indirect Diffuse
-
RenderMan Logarithm
-
RenderMan Occlusion
-
RenderMan Ray Information
-
RenderMan Render State Information
-
RenderMan Shadow Map
-
RenderMan Step
-
RenderMan Surface Color
-
RenderMan Texture Map
-
RenderMan Texture Map Information
-
RenderMan Transform
-
RenderMan Transform Color
-
RenderMan Z-Depth From Camera
-
Reorder
Reorders items in an array or string.
-
Report Error
Optionally report a custom VEX error or warning.
-
Reshape Value
Modulates input value using a variety of methods.
-
Resolution
Returns the pixel resolution of an input.
-
Resolve Mapping Attribute
Resolves a mapping dictionary attribute to a KineFX point number.
-
Rest Position
Checks if the geometry attribute rest is bound and, if so, uses it
as the rest position for shading.
-
Return
Generates a return statement inside a method or a function defined by the parent subnet.
-
Reverse
Adds an item to an array or string.
-
Reverse Foot
Rotates the foot around custom pivots specific to a reverse foot KineFX set-up.
-
Rings
Generates repeating filtered rings.
-
Ripples
Generates repeating ripples.
-
Rotate
Applies a rotation by 'angle' radians to the given 3×3 or 4×4
matrix.
-
Rotate by Quaternion
Rotates a vector by a quaternion.
-
Round to Integer
Rounds the argument to the closest integer.
-
Rounded Hexes
Generates repeating filtered rounded hexagons.
-
Rounded Stars
Generates repeating filtered rounded five-pointed stars.
-
Run External Program Procedural
This procedural will run an external application in order to generate geometry at render time.
-
SSS Component
Adds energy conservation functionality and additional controls to the Physical SSS VOP.
-
Sample Sphere
Samples the interior or surface of the unit circle, sphere, or hypersphere, within a max angle of a direction.
-
Scale
Scales a 3×3 or 4×4 matrix by 'amount' units along the x,y, and z
axes.
-
Scales
Generates a scale-like pattern and returns the displaced position,
normal, and displacement amount.
-
Set Agent Clip Names
Sets the current animation clips for an agent primitive.
-
Set Agent Clip Times
Sets the current times for an agent primitive’s animation clips.
-
Set Agent Clip Weights
Sets the blend weights for an agent primitive’s animation clips.
-
Set Agent Layer
Sets the current layers or collision layers of an agent primitive.
-
Set Agent Transforms
Overrides the transforms of an agent primitive.
-
Set Attribute
-
Set CHOP Attribute
Sets a CHOP attribute value.
-
Set Channel Tranform
Sets a transform value when evaluating a Channel VOP in Tranlate/Rotate/Scale mode.
-
Set Channel Value
Sets a channel value when evaluating a Channel VOP in Channel/Sample modes.
-
Set Dictionary Element
Sets the value at the specified key.
-
Set Element
Sets the element at the specified index.
-
Set Layer Component
Sets a layer’s components to new values.
-
Set Layer Export
Adds layer exports to the Shader Layer struct
-
Set Matrix Component
Assigns a value to one of the matrix’s components.
-
Set Matrix2 Component
Assigns a value to one of the matrix2's components.
-
Set Matrix3 Component
Assigns a value to one of the matrix3's components.
-
Set Point Transform
Sets one point transform at a given point ID.
-
Set Point Transforms
Sets arrays of point transforms at an array of point IDs.
-
Set Primitive Vertex
-
Set Vector Component
Assigns a value to one of the vector’s components.
-
Set Vector2 Component
Assigns a value to one of the vector2's components.
-
Set Vector4 Component
Assigns a value to one of the vector4's components.
-
Shader Output Export Variables
Represents export parameters in a shader call.
-
Shader Output Global Variables
Represents global variables that are bound as output parameters in a shader call.
-
Shading Area
Computes the shading area of the given variable.
-
Shading Derivative
Computes the derivative of a given variable with respect to the s or
t parametric coordinate.
-
Shading Layer Parameter
Creates a parameter to appear in the signature of the VEX function
defined by the VOP network (VOPNET).
-
Shading Normal
Computes the normal at the location specified by the P position.
-
Shadow
This shader calls the shadow shader inside an illuminance loop.
-
Shadow Map
Shadow Map treats the depth map as if the image were rendered from a
light source.
-
Shadow Matte
Implements a shadowmatte shader that occludes geometry behind the
surface being rendered.
-
Sign
Returns -1 if the input is less than 0, otherwise it returns 1.
-
Sine
Performs a sine function.
-
Skin Shader Core
A skin shader with three levels of subsurface scattering.
-
Sky Box
Creates a sky noise pattern with volumetric clouds.
-
Slice
Slices a sub-string or sub-array of a string or array.
-
Smooth
Computes a number between zero and one.
-
Smooth Rotation
Returns the closest equivalent Euler rotations to a reference rotation.
-
Snippet
Runs a VEX snippet to modify the incoming values.
-
Soft Clip
Increases or decreases contrast for values at the top of the input range.
-
Soft Dots
Generates repeating soft dots.
-
Sort
Returns the array sorted in increasing order.
-
Specular
Generates a color using the selected specular lighting model calculation.
-
Specular Sheen
Generates a color using a specular lighting model with a Fresnel falloff calculation.
-
Spherical Linear Interp
Computes a spherical linear interpolation between its two quaternion
inputs, and outputs the intermediate quaternion.
-
Splatter
Generates a splatter pattern and returns the splatter amount.
-
Spline
Computes either a Catmull-Rom (Cardinal) spline or a Linear spline
between the specified key points, given an interpolant (u)
in the domain of the spline.
-
Split String
Splits a string into tokens.
-
Sprites Procedural
This procedural will render points as sprites.
-
Square Root
Computes the square root of the argument.
-
Starts With
Result 1 if the string starts with the specified string.
-
Stash Transform
Stashes a KineFX transform matrix as a constant.
-
String Length
Returns the length of the string.
-
String to Character
Converts an UTF8 string into a codepoint.
-
Strip
Strips leading and trailing whitespace from a string.
-
Stripes
Generates repeating filtered stripes.
-
Struct
Creates, modifies, or de-structures an instance of a structured datatype.
-
Struct Pack
Bundles input values into an instance of an ad-hoc struct.
-
Struct Unpack
Extracts one or more values from a struct by member name.
-
Sub Network
Contains other VOP operators.
-
Subnet Connector
Represents an input or an output (or both) of the parent VOP subnet.
-
Subnet Input
Allows the connection of operators outside a subnet to operators
inside the subnet.
-
Subnet Output
Allows the connection of operators inside a subnet to operators
outside the subnet.
-
Subtract
Outputs the result of subtracting all its inputs.
-
Subtract Constant
Subtracts the specified constant value from the incoming integer, float,
vector or vector4 value.
-
Surface Color
Generates a basic color with a choice of tinting with the point color and/or a color map.
-
Surface Distance
Finds the shortest distance between a point and a source point group.
-
Switch
Switches between network branches based on the value of an input.
-
Switch Lighting BSDF
Use a different bsdf for direct or indirect lighting.
-
Swizzle Vector
Rearranges components of a vector.
-
Swizzle Vector2
Rearranges components of a vector2.
-
Swizzle Vector4
Rearranges components of a vector4.
-
Tangent
Performs a tangent function.
-
Tangent Normal
Transform an input normal to UV/tangent space
-
Tangent Normal Remap
Transform an input normal from UV/tangent to current space
-
Tangent Normals
Exports shader normals as a render plane.
-
Tetrahedron Adjacent
Returns primitive number of an adjacent tetrahedron.
-
Tetrahedron Adjacent
Returns vertex indices of each face of a tetrahedron.
-
Texture
Computes a filtered sample of the texture map specified and returns
an RGB or RGBA color.
-
Texture 3D
Returns the value of a 3D image at a specified position within that
image.
-
Texture 3D Box
Queries the 3D texture map specified and returns the bounding box
information for the given channel in the min and max corner
vectors.
-
Texture Map
-
Thin Film Fresnel
Computes the thin film reflection and refraction contributions given a normalized incident ray, a normalized surface normal, and an index of refraction.
-
Tiled Boxes
Generates staggered rectangular tiles.
-
Tiled Hexagons
Generates staggered hexagonal tiles.
-
Timing
Returns the frame range and rate of the given input.
-
Title Case
Returns a string that is the titlecase version of the input string.
-
To Lower
Returns a string that is the lower case version of the input string.
-
To NDC
Transforms a position into normal device coordinates.
-
To NDC
-
To Polar
Converts cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates.
-
To Upper
Returns a string that is the upper case version of the input string.
-
Trace
Uses the vex gather function to send a ray and return with the reflected or refracted colors.
-
Transform
Transforms a vector to or from an object’s transform space, or one of several other spaces, such as world or camera space.
-
Transform From Path
Constructs a KineFX transform matrix from a position on a path.
-
Transform From Surface
Constructs a KineFX transform matrix from a position on a geometry’s surface.
-
Transform Matrix
-
Translate
Translates a 4×4 matrix 'amount' units along the x,y,z and possibly w
axes.
-
Transpose
-
Trigonometric Functions
Performs a variety of trigonometric functions.
-
Turbulent Noise
Can compute three types of 1D and 3D noise with the ability to compute turbulence with roughness and attenuation.
-
Two Bone IK
Perform a simple two-bone IK solve
-
Two Sided
Generates a two sided surface.
-
Two Way Switch
Takes an integer input.
-
USD Global Variables
Provides outputs representing commonly used input variables for processing USD primitive attributes inside an Attribute VOP LOP.
-
USD Preview Surface
USD Preview Surface shader
-
USD Prim Var Reader
-
USD Prim Var Reader
USD Prim Var Reader shader
-
USD Transform 2D
-
USD Transform 2D
Represents a standard USD primitive for transforming texture co-ordinates.
-
USD UV Texture
Represents a standard USD primitive for looking up texture values.
-
UV Coords
Returns texture coordinates or geometric s and t, depending on what is defined.
-
UV Noise
Disturbs the incoming parametric s and t coordinates using anti aliased noise generated from the Surface Position input.
-
UV Planar Project
Computes UV co-ordinates projected along a single axis, derived from the position of an object, and generates a mask relative to the projection axis.
-
UV Position
-
UV Project
Assigns texture coordinates based on the specified projection
type.
-
UV Transform
Transforms texture coordinates by the inverse of the matrix
consisting of the translation, rotation, and scale amounts.
-
UV Tri-planar Project
Projects texture maps along X, Y, and Z axes and blends them together at the seams.
-
Undulatus
Generates a 2D, wave like cloud pattern.
-
Unified Noise
Presents a unified interface and uniform output range for all the noise types available in VEX.
-
Unified Noise Static
Presents a unified interface and uniform output range for all the noise types available in VEX.
-
Unique Value Count of Attribute
-
Unique Values of Attribute
-
VOP Force Global
Provides outputs that represent all the global variables for the
Force VOP network type.
-
VOP Force Output Variables
Simple output variable for VOP Force Networks.
-
Vector Cast
Converts between different vector types.
-
Vector To Float
Unpacks a vector into its three components.
-
Vector To Quaternion
Takes an angle/axis vector and constructs the quaternion representing the rotation about that axis.
-
Vector To Vector4
Converts a vector to a vector4.
-
Vector to Matrix3
Converts rows values to a 3×3 matrix value.
-
Vector to Vector2
Converts a vector to a vector2 and also returns the third component of the vector.
-
Vector2 To Float
Unpacks a vector2 into its two components.
-
Vector2 To Vector
Converts a vector2 to a vector.
-
Vector2 To Vector4
Converts a pair of vector2s into a vector4.
-
Vector2 to Matrix2
Converts rows values to a 2×2 matrix value.
-
Vector4 to Float
Unpacks a vector4 into its four components.
-
Vector4 to Matrix
Converts rows values to a 4×4 matrix value.
-
Vector4 to Vector
Converts a vector4 to a vector and also returns the fourth component
of the vector4.
-
Vector4 to Vector2
Converts a vector4 to a pair of vector2s..
-
Veins
Generates an anti-aliased vein pattern that can be used in any VEX
context.
-
Vex Volume Procedural
This procedural will generate a volume from a CVEX shader.
-
Visualize
Exports a vis_ prefixed attribute.
-
Volume Density to Opacity
Computes the opacity of a uniform volume given a density.
-
Volume Gradient
Calculates the gradient of a volume primitive stored in a disk
file.
-
Volume Index
Gets the value of a voxel from a volume primitive stored in a disk file.
-
Volume Index To Pos
Calculates the position of a voxel in a volume primitive stored in
a disk file.
-
Volume Index Vector
Gets the vector value of a voxel from a volume primitive stored in a disk file.
-
Volume Model
A shading model for volume rendering.
-
Volume Pos To Index
Calculates the voxel closest to a voxel of a volume primitive stored in
a disk file.
-
Volume Resolution
Gets the resolution of a volume primitive stored in a disk file.
-
Volume Sample
Samples the value of a volume primitive stored in a disk file.
-
Volume Sample Vector
Samples the vector value of a volume primitive stored in a disk file.
-
Volume VOP Global Parameters
Provides outputs that represent all the global variables for the
Volume VOP network type.
-
Volume VOP Output Variables
Simple output variable for Volume VOP Networks.
-
Voronoi Noise
Computes 1D, 3D, and 4D Voronoi noise, which is similar to Worley
noise but has additional control over jittering.
-
Wave Vector
Computes the wave vector for a given index in a grid of specified size.
-
Waves
Simulates rolling waves with choppiness of various frequencies, and
outputs the positional and normal displacements as well
as the amount of displacement.
-
Wire Pattern
Returns float between 0 and 1 which defines a wire grid pattern useful for simulating screens or visualizing parametric or texture coordinates.
-
Worley Noise
Computes 1D, 3D, and 4D Worley noise, which is synonymous with cell
noise.
-
XPU Pyro Preview
Simplified smoke, fire, and explosions shader for Karma XPU.
-
XYZ Distance
Finds closest position on a primitive in a given geometry file.
-
Xor
Performs a logical xor operation between its inputs.
-
_lensshader_common
-
argsort
Returns the indices of a sorted version of an array.
-
mtlxopen_pbr_surface_to_standard_surface
Conversion of Open PBR node to the Standard Surface Node
-
mtlxstandard_surface_to_open_pbr_surface
Conversion of Standard Surface Node To Open PBR
-
roundededge
Blends the normals between faces within specified radius.

MtlX Mix VOPs.
MtlX Normalmap, to transform them to -1 to 1 range.
Render Geometry Settings to Enable Caustics on specific objects.
Render Geometry Settings, to render more efficiently with Karma.


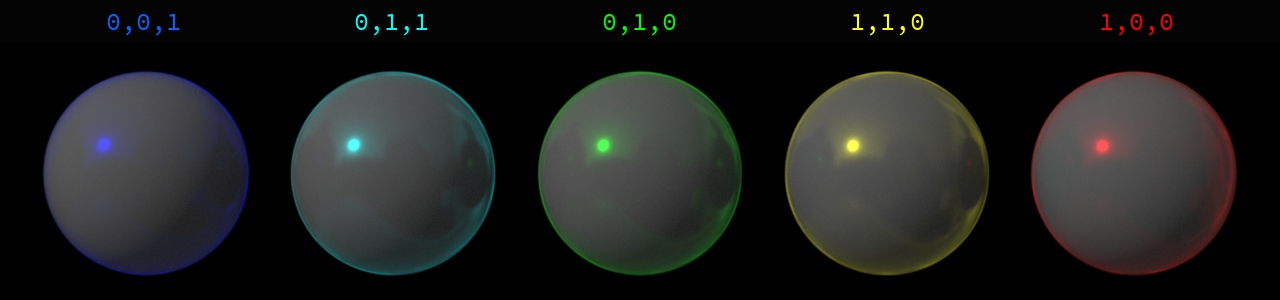
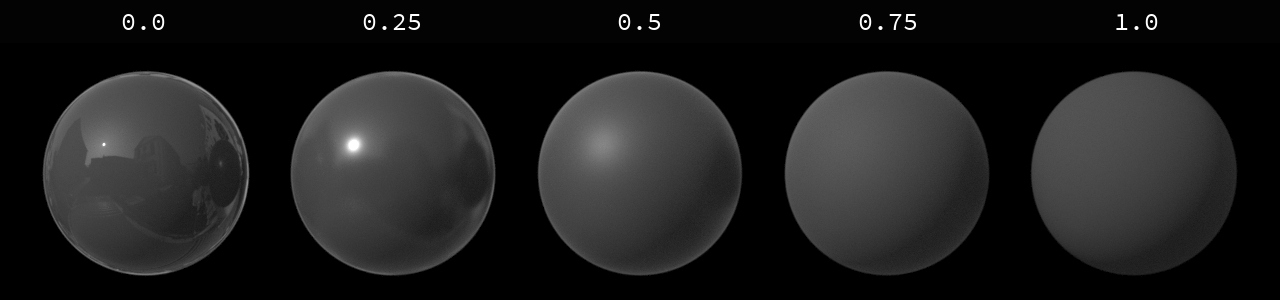
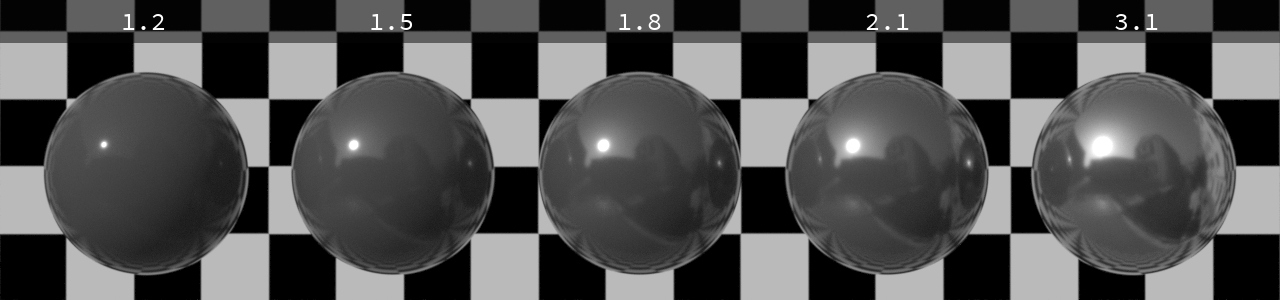

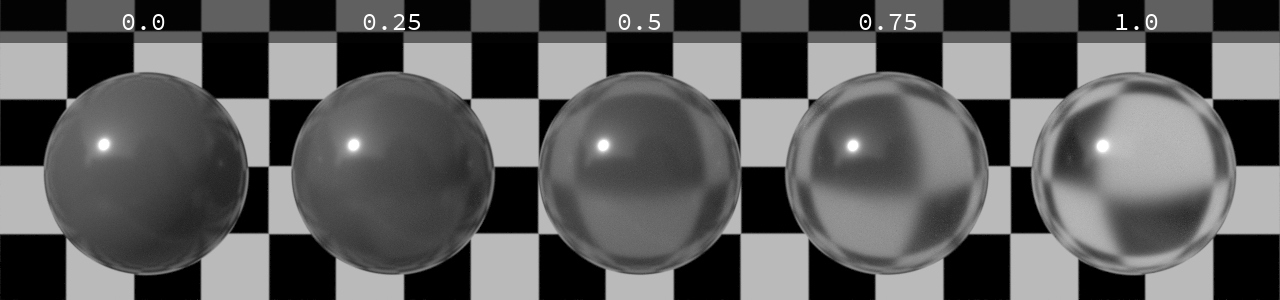


Not Supported by Karma.
Not Supported by Karma.